Trajectory Analysis with Monocle 3
Monocle, from the Trapnell Lab, is a piece of the TopHat suite (for RNAseq) that performs among other things differential expression, trajectory, and pseudotime analyses on single cell RNA-Seq data. A very comprehensive tutorial can be found on the Trapnell lab website. We will be using Monocle3, which is still in the “beta” phase of its development and hasn’t been updated in a few years. The development branch however has some activity in the last year in preparation for Monocle3.1.
library(monocle3)
library(Seurat)
library(SeuratWrappers)
library(patchwork)
#library(dplyr)
set.seed(1234)
I prefer to use a few custom colorblind-friendly palettes, so we will set those up now. The palettes used in this exercise were developed by Paul Tol. You can learn more about them on Tol’s webpage.
tol_high_contrast_palette <- c("#DDAA33", "#BB5566", "#004488")
tol_vibrant_palette <- c("#0077BB", "#33BBEE", "#009988",
"#EE7733", "#CC3311", "#EE3377",
"#BBBBBB")
tol_muted_palette <- c("#332288", "#88CCEE", "#44AA99",
"#117733", "#999933", "#DDCC77",
"#CC6677", "#882255", "#AA4499")
Project set-up
Because Seurat is now the most widely used package for single cell data analysis we will want to use Monocle with Seurat. For greater detail on single cell RNA-Seq analysis, see the Introductory course materials here.
Loading data into Seurat
data_location <- "data_download/"
samples <- c("sample1", "sample2", "sample3")
raw10x <- lapply(samples, function(i){
d10x <- Read10X_h5(file.path(data_location, paste0(i, "_raw_feature_bc_matrix.h5")))
colnames(d10x$`Gene Expression`) <- paste(sapply(strsplit(colnames(d10x$`Gene Expression`),split="-"),'[[',1L),i,sep="-")
colnames(d10x$`Antibody Capture`) <- paste(sapply(strsplit(colnames(d10x$`Antibody Capture`),split="-"),'[[',1L),i,sep="-")
d10x
})
Genome matrix has multiple modalities, returning a list of matrices for this genome
Genome matrix has multiple modalities, returning a list of matrices for this genome
Genome matrix has multiple modalities, returning a list of matrices for this genome
names(raw10x) <- samples
trA <- CreateSeuratObject(do.call("cbind", lapply(raw10x,"[[", "Gene Expression")),
project = "cellranger multi",
min.cells = 0,
min.features = 300,
names.field = 2,
names.delim = "\\-")
trA$percent_mito <- PercentageFeatureSet(trA, pattern = "^MT-")
trA <- subset(trA, percent_mito <= 10)
trA <- subset(trA, nCount_RNA <= 10000)
trA <- subset(trA, nFeature_RNA >= 500)
table(trA$orig.ident)
sample1 sample2 sample3
1855 999 1200
Seurat processing of data
Because we don’t want to do the exact same thing as we did in the Velocity analysis, lets instead use the Integration technique.
# First split the sample by original identity
trA.list <- SplitObject(trA, split.by = "orig.ident")
# perform standard preprocessing on each object
for (i in 1:length(trA.list)) {
trA.list[[i]] <- NormalizeData(trA.list[[i]], verbose = FALSE)
trA.list[[i]] <- FindVariableFeatures(
trA.list[[i]], selection.method = "vst",
nfeatures = 2000, verbose = FALSE
)
}
features <- SelectIntegrationFeatures(trA.list)
for (i in seq_along(along.with = trA.list)) {
trA.list[[i]] <- ScaleData(trA.list[[i]], features = features)
trA.list[[i]] <- RunPCA(trA.list[[i]], features = features)
}
Centering and scaling data matrix
PC_ 1
Positive: PCLAF, CST7, NKG7, RRM2, CCL5, GZMA, GZMH, PTTG1, ACTB, GZMB
S100A4, LGALS1, MKI67, ANXA2, BIRC5, IL32, TK1, CENPM, GZMK, CCNA2
CLSPN, CDC20, GNLY, PLEK, CLIC1, CYTOR, GINS2, TPX2, TMSB4X, CD99
Negative: EEF1A1, RPL13, RPL18A, RPS8, RPS3A, RPS18, TPT1, RPS12, RPS23, RPS5
RPS6, EEF1B2, RPL7A, RPL8, RPS16, RPLP2, RPL17, LTB, LINC02446, RPLP0
TCF7, IL7R, SNHG29, FOS, NELL2, RPL37A, RPL4, CCR7, RPL7, RPSA
PC_ 2
Positive: RPLP0, RPS8, LDHB, RPS5, SNHG29, RPS6, RPL4, RRM2, RPS3A, NPM1
RPS18, PCLAF, RPS16, TMSB10, SLC25A5, STMN1, RPL7, EEF1B2, AIF1, RPS23
RPL18A, VIM, CCR7, RPL37A, RPSA, TUBB, CCNA2, EEF1A1, GINS2, TKT
Negative: CST7, NKG7, GNLY, CCL5, GZMK, GZMA, CTSW, IL32, HOPX, TRDV2
KLRD1, TRGV9, FGR, KLRG1, NCR3, S100A4, TYROBP, LYAR, XCL2, PLEK
MT-CYB, CD74, DUSP2, MYO1F, XCL1, MAP3K8, BHLHE40, FCRL3, KLRC2, GZMH
PC_ 3
Positive: KLRB1, GZMA, RPL13, KLRG1, PLEK, RPS12, ZBTB16, CXCR6, TRDV2, TRAV1-2
SLC4A10, EEF1A1, RPLP0, RPL17, GZMH, TGFBR3, RPS8, KLRC1, BHLHE40, RPS18
TRBV6-4, PRF1, TRGV9, GZMB, RPL18A, ALOX5AP, MYC, AC245014.3, IL18RAP, CD160
Negative: IFITM1, TMSB10, ZNF683, TMSB4X, MT-CO2, MT-CYB, KLRC2, XCL1, MT-CO1, CXCR3
IFITM2, CD52, CTSW, XCL2, MT-CO3, ACTB, FUT7, MT-ND4, IFITM3, LINC02446
TCF7, KLRC3, LGALS1, FCRL3, KLRC4, FCER1G, ITM2C, SLFN5, PLAC8, MT-ATP6
PC_ 4
Positive: RRM2, CCNA2, ASPM, DHFR, ASF1B, KLRC2, MT-ND4L, PKMYT1, RAD51, ZWINT
XCL1, CDCA8, CENPM, MT-CYB, KIF2C, AURKB, KNL1, NDC80, UBE2C, XCL2
NUSAP1, KIF14, CTSW, KIFC1, DIAPH3, HMMR, MT-CO2, CDK1, MKI67, TK1
Negative: ACTG1, ACTB, KLRB1, EIF4A1, MYH9, PSMB10, GZMA, CORO1A, ATP5F1B, PSME2
HSP90AB1, S100A6, CD28, GAPDH, EWSR1, LCP1, SH3BGRL3, GZMH, FLNA, ENO1
ACTR3, AQP3, NPM1, DENND2D, CNN2, LDHB, PSMB8, DYNLL1, SAT1, NDUFB3
PC_ 5
Positive: PTTG1, CDC20, BIRC5, HLA-DRA, CDKN3, LGALS1, FGFBP2, CENPF, CCNB1, CYTOR
HLA-DRB1, GZMH, TROAP, TPX2, CD38, CENPE, PLK1, GZMA, LAG3, CX3CR1
MND1, MKI67, HLA-DPB1, ANXA2, CD8B, HIST1H2BH, HLA-DRB5, HMMR, ZEB2, CCL4
Negative: IFITM2, CTSW, FOS, LTB, IFITM1, NCR3, XCL1, LST1, GINS2, CRIP1
MCM2, ATAD5, DTL, HSP90AB1, DDIT4, TRBV20-1, HELLS, MIF, IL32, FAM111B
JUNB, MT-ND5, MAP3K1, S100A4, FCER1G, IFITM3, MT-ND1, HSP90AA1, TIMP1, TCF19
Centering and scaling data matrix
PC_ 1
Positive: CCL5, RPL13, TPT1, RPS12, RPL18A, EEF1A1, IFITM1, GZMK, LTB, ZFP36
RPS23, FOS, KLRB1, CD74, RPL7A, ZNF331, SLC2A3, KLF6, CD27, MT-CO1
NR4A2, IL7R, SLFN5, JUN, RPS18, CST7, KLRG1, TNFAIP3, TENT5C, PDCD4
Negative: TUBA1B, RRM2, STMN1, H2AFZ, TUBB, PCNA, PCLAF, MCM7, HMGB2, CENPM
RAN, DUT, HIST1H4C, GINS2, DNAJC9, PTMA, HMGN2, TPI1, TK1, FABP5
FEN1, DHFR, MCM5, CENPW, GAPDH, ZWINT, CLSPN, ASF1B, MCM3, NASP
PC_ 2
Positive: TMSB4X, ACTG1, ACTB, CAPG, PLAC8, CNN2, RPLP0, VIM, HSP90AB1, PRDX1
PPIA, S100A6, PSMA5, NME2, GAPDH, HNRNPA1, SELL, ANXA2, PPIB, CFL1
TMSB10, HMGN2, MYL6, MRPL51, ATP5MC3, DANCR, SLC25A5, PSME2, EIF4A1, CCT5
Negative: NUSAP1, SPC25, CDK1, HIST1H1B, HIST1H2AJ, UBE2C, CDCA8, KIFC1, HIST1H2AI, NKG7
HIST1H4C, KIF23, RRM2, CDCA5, ASPM, CKS2, NDC80, TOP2A, ARHGAP11A, CCNA2
CCL5, CKAP2L, GZMA, GZMH, NCAPG, PKMYT1, TPX2, CKS1B, TTK, HJURP
PC_ 3
Positive: GZMH, NKG7, GZMA, GZMB, GNLY, SH3BGRL3, CCL5, S100A4, FGFBP2, IL32
CST7, HOPX, KLRD1, ANXA1, CRIP1, LGALS1, PRF1, CLIC3, CFL1, SPON2
APOBEC3G, LY6E, CTSW, BHLHE40, CD99, CD52, PPIB, CCL4, ACTB, CD63
Negative: RPS12, EEF1A1, TCF7, RPL13, LTB, RPS18, CCR7, RPL18A, PLAC8, RPS8
SELL, LEF1, RPS5, RPS23, RPS3A, CAPG, RPLP2, RPL7A, NOSIP, EEF1B2
AC004585.1, NELL2, RPLP0, RPL4, RPL8, RPL17, TPT1, AQP3, IL7R, ARMH1
PC_ 4
Positive: PLK1, CCNB1, CDC20, DLGAP5, CDCA8, TMSB4X, CCNB2, CENPF, CDCA3, NEK2
TPX2, UBE2C, KIF14, ASPM, BIRC5, PTTG1, HMMR, AURKB, CDKN3, ACTG1
ACTB, KIF20A, TMSB10, TOP2A, ARL6IP1, CENPE, RACGAP1, DEPDC1B, DIAPH3, KIF23
Negative: GINS2, RPL18A, RPS12, RPL13, EEF1A1, RPS8, RPS23, MCM10, RPL8, UNG
CDC45, MSH6, RPS6, RPS18, MCM3, MCM7, PCNA, C19orf48, DTL, MCM4
FEN1, MCM6, GNLY, CDCA7, FTL, FAM111B, MCM2, RPL17, RPLP0, RPL7A
PC_ 5
Positive: MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3, MT-CYB, FLNA, MT-ATP6, HIST1H1E, COTL1, MT-ATP8, MT-ND5
MT-ND4L, MYH9, MT-ND6, RPS2, MT-ND4, HNRNPU, LGALS1, MT-ND1, HMGA1, MSN
MTA2, AC011446.2, CD81, ACTN4, AC005944.1, MYO1G, CDT1, AL133415.1, PLEC, RASSF2
Negative: CDC20, PLK1, CCNB1, CDKN3, RPL18A, IFITM1, KIF20A, KIF14, KPNA2, RPS3A
CCNB2, EEF1A1, LDHA, RPS23, FTL, RPL7A, PTMA, NEK2, RPL8, KLRB1
TUBB4B, NKG7, RPL17, CKS1B, CTSW, HSP90B1, RPS8, KLRD1, CDCA3, PTTG1
Centering and scaling data matrix
PC_ 1
Positive: CCL5, NKG7, IFITM1, CST7, CD52, ZFP36, SH3BGRL3, ZNF683, IL7R, LTB
FGFBP2, KLRB1, FOS, TPT1, KLRG1, TNFAIP3, SLFN5, SLC2A3, JUN, TMSB4X
TRBV28, ZNF331, S100B, ALOX5AP, CCL4, TCF7, TRAV17, DDIT4, GZMH, PATL2
Negative: TUBA1B, RRM2, STMN1, H2AFZ, TUBB, HMGB2, PCLAF, FABP5, MCM7, FEN1
RAN, HIST1H4C, GAPDH, PCNA, HMGN2, PTMA, CLSPN, CENPM, CENPW, DHFR
TXN, PTTG1, RPA3, SMC2, HMGB1, HSPD1, TPI1, TUBB4B, GMNN, GINS2
PC_ 2
Positive: GZMK, RPS12, RPS18, EEF1A1, RPS8, RPL18A, RPS23, RPL7A, LEF1, RPL8
RPS3A, RPS5, RPS6, CD28, CPNE2, CD27, RPLP0, LTB, RPLP2, PLAC8
SNHG29, TCF7, CNN2, AIF1, DANCR, LIMS1, CCR7, NME2, RPL17, SELL
Negative: GZMB, NKG7, FGFBP2, GZMH, GNLY, GZMA, PRF1, S100A4, CCL4, UBE2C
SH3BGRL3, SPON2, CX3CR1, NUSAP1, KIFC1, CRIP1, CDK1, TPX2, HIST1H4C, CCL5
CST7, RACGAP1, TOP2A, RRM2, CENPE, CKS1B, CKAP2L, CENPF, PLEK, TUBB4B
PC_ 3
Positive: GZMB, GZMH, S100A4, PRF1, LGALS1, GNLY, GZMA, S100A11, SH3BGRL3, NKG7
S100A6, ANXA2, FGFBP2, CX3CR1, PLEK, PPIB, HOPX, ANXA1, SPON2, PSME2
APOBEC3G, HSP90AB1, LY6E, IL32, HSPA5, IFITM2, DCTPP1, HSP90B1, LGALS3, GAPDH
Negative: UBE2C, TOP2A, CDK1, NUSAP1, GZMK, TPX2, HIST1H2AI, JUN, KIFC1, KIF23
PLK1, HIST1H3D, HIST1H2AJ, CDCA2, ANLN, TCF7, RACGAP1, CDCA3, HIST1H4C, CDCA8
SPC25, HIST1H3C, HIST1H3B, HIST2H2AB, KIF22, ASPM, AURKB, GTSE1, CENPF, CENPE
PC_ 4
Positive: CCNB1, CDC20, PTTG1, ACTG1, CCNB2, TMSB4X, CENPF, PLK1, IFITM1, HMGB3
CDKN3, DLGAP5, TPX2, TROAP, ARL6IP1, HMMR, CLIC1, LGALS1, ANP32E, ANXA2
BIRC5, PIMREG, JPT1, ASPM, AURKB, IFIT3, KNSTRN, HSPA5, CENPE, DYNLL1
Negative: MCM7, GINS2, PCNA, MCM5, ATAD2, MCM3, MCM4, FEN1, CDC45, CLSPN
PCLAF, DHFR, FAM111B, MCM2, LIG1, TCF19, RAD51, DTL, TMEM106C, MCM6
C19orf48, SIVA1, POLA2, RNASEH2A, CENPM, UHRF1, CENPX, DUT, RRM2, DNAJC9
PC_ 5
Positive: FOS, IL32, HLA-DRB5, CD74, IFITM1, TMSB4X, EEF1A1, ITM2A, LTB, PPIA
JUN, ALOX5AP, CD160, PSME2, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, LDHB, PGK1, ZWINT, HLA-DRA
SLC25A5, ACTG1, CD99, XCL2, CFL1, PPP1CA, CTSW, XCL1, HSPB11, TALDO1
Negative: MT-CO1, RPS2, MT-CO2, FLNA, MT-ND5, MT-ND6, MT-ATP6, ABHD17A, LGALS3, MT-CO3
FKBP4, AHNAK, MT-CYB, GZMB, VIM, AL138963.4, GNLY, MT-ND4L, MT-ND4, VPS4A
ESYT2, AC004687.1, IDH2, SF3B3, NSD2, HNRNPU, MT-ND1, GPR180, VCL, TPM4
# find anchors
anchors <- FindIntegrationAnchors(object.list = trA.list)
Computing 2000 integration features
Scaling features for provided objects
Finding all pairwise anchors
Running CCA
Merging objects
Finding neighborhoods
Finding anchors
Found 4259 anchors
Filtering anchors
Retained 1620 anchors
Running CCA
Merging objects
Finding neighborhoods
Finding anchors
Found 5045 anchors
Filtering anchors
Retained 1395 anchors
Running CCA
Merging objects
Finding neighborhoods
Finding anchors
Found 3975 anchors
Filtering anchors
Retained 1807 anchors
# integrate data
trA.integrated <- IntegrateData(anchorset = anchors)
Merging dataset 2 into 3
Extracting anchors for merged samples
Finding integration vectors
Finding integration vector weights
Integrating data
Merging dataset 1 into 3 2
Extracting anchors for merged samples
Finding integration vectors
Finding integration vector weights
Integrating data
trA.integrated <- ScaleData(trA.integrated)
Centering and scaling data matrix
trA.integrated <- RunPCA(trA.integrated)
PC_ 1
Positive: RRM2, TUBA1B, STMN1, PCLAF, H2AFZ, HMGB2, TUBB, FABP5, MCM7, FEN1
CLSPN, CENPW, DHFR, CENPM, PCNA, UBE2T, PTTG1, GMNN, HIST1H4C, GINS2
SMC2, PTMA, ZWINT, TUBB4B, HMGN2, RPA3, LMNB1, TXN, CKS1B, RAN
Negative: CCL5, CST7, NKG7, IFITM1, CD160, ZNF683, LTB, TPT1, SLFN5, TRBV28
ZFP36, CD52, FOS, SLC2A3, PATL2, IL7R, FCRL3, EEF1A1, TMSB4X, JUN
ZEB2, TRAV17, MAF, TNFAIP3, SH3BGRL3, ALOX5AP, KLRG1, RPL18A, IL10RA, TRBV5-6
PC_ 2
Positive: GZMK, RPS12, EEF1A1, RPS18, RPL18A, RPS8, RPS23, RPL8, RPS3A, RPS6
RPL7A, RPLP2, RPL13, RPS5, RPLP0, EEF1B2, CNN2, RPL17, PLAC8, LIMS1
CD27, CD28, LTB, LEF1, NOSIP, NME2, SELL, SNHG29, MT-CO3, DANCR
Negative: GZMB, FGFBP2, GZMH, GNLY, CCL4, GZMA, PRF1, NKG7, CX3CR1, SPON2
S100A4, CST7, UBE2C, PLEK, NUSAP1, SH3BGRL3, KIFC1, CDK1, ASPM, CLIC3
HOPX, CCL5, LGALS1, KLRD1, TPX2, CRIP1, S100A11, HIST1H4C, CKAP2L, CENPE
PC_ 3
Positive: GZMB, LGALS1, GZMH, PRF1, GNLY, GZMA, S100A11, S100A4, ANXA2, PLEK
FGFBP2, PPIB, NKG7, S100A6, APOBEC3G, CX3CR1, ACTB, HOPX, SPON2, IL32
HSPA5, ANXA1, HSP90AB1, SH3BGRL3, DCTPP1, S100A10, CCT5, PSME2, IFI30, LGALS3
Negative: UBE2C, TOP2A, CDK1, NUSAP1, CDCA8, KIFC1, HIST1H2AI, HIST1H2AJ, TPX2, SPC25
CDCA3, KIF23, ASPM, CDCA2, HIST1H3C, PLK1, DIAPH3, RACGAP1, HIST1H1B, HIST1H4C
HJURP, CDCA5, HIST1H3D, GTSE1, JUN, HIST1H3B, HIST2H2AB, CKAP2L, KIF15, ANLN
PC_ 4
Positive: CDC20, CCNB1, PLK1, CCNB2, PTTG1, CENPF, DLGAP5, ACTG1, CDKN3, TMSB4X
TPX2, HMMR, AURKB, BIRC5, TROAP, ASPM, CENPE, KNSTRN, PIMREG, ARL6IP1
HMGB3, JPT1, KIF14, NEK2, NUF2, KIF20A, DEPDC1B, TUBA1C, ANP32E, DYNLL1
Negative: GINS2, MCM7, PCNA, CDC45, MCM4, MCM5, ATAD2, FAM111B, CLSPN, MCM2
MCM3, TCF19, FEN1, DTL, MCM10, MCM6, RAD51, UHRF1, DHFR, LIG1
HELLS, TMEM106C, POLA2, CHEK1, RBBP8, CDC6, CCNE2, BRCA2, PCLAF, RFC2
PC_ 5
Positive: CCNB1, CDC20, CDKN3, RPS12, CCNB2, PLK1, NOP16, RPS8, BIRC5, RPS3A
DLGAP5, KNSTRN, HPDL, GNLY, RPS23, NUF2, GZMB, RPL8, SPON2, DEPDC1B
HMMR, DCTPP1, KIF14, ALYREF, RPL18A, NPM3, TROAP, MRPL18, HMGB3, CEP57L1
Negative: IL32, TMSB4X, HIST1H1D, ACTG1, UCP2, HIST1H2AL, CD74, DENND2D, PPP1CA, HIST1H3B
CORO1A, HLA-DRA, APOBEC3G, CFL1, CHI3L2, FOS, HIST1H2AJ, HIST1H1C, LIMS1, XCL2
CD52, ATP5F1B, HIST1H1E, ACTB, CXCR3, CCL5, LDHB, HIST1H1B, HLA-DRB5, GZMK
trA.integrated <- RunUMAP(trA.integrated, dims = 1:50, reduction.name = "UMAP")
12:28:33 UMAP embedding parameters a = 0.9922 b = 1.112
12:28:33 Read 4054 rows and found 50 numeric columns
12:28:33 Using Annoy for neighbor search, n_neighbors = 30
12:28:33 Building Annoy index with metric = cosine, n_trees = 50
0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100%
[----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|
**************************************************|
12:28:33 Writing NN index file to temp file /var/folders/c6/zbknwx5d7wlfqhgpy83jlg1h0000gp/T//Rtmp7T0tKt/file8dd41f34a188
12:28:33 Searching Annoy index using 1 thread, search_k = 3000
12:28:35 Annoy recall = 100%
12:28:35 Commencing smooth kNN distance calibration using 1 thread
12:28:37 Initializing from normalized Laplacian + noise
12:28:37 Commencing optimization for 500 epochs, with 189498 positive edges
12:28:43 Optimization finished
trA.integrated <- FindNeighbors(trA.integrated, dims = 1:50)
Computing nearest neighbor graph
Computing SNN
trA.integrated <- FindClusters(trA.integrated)
Modularity Optimizer version 1.3.0 by Ludo Waltman and Nees Jan van Eck
Number of nodes: 4054
Number of edges: 297149
Running Louvain algorithm...
Maximum modularity in 10 random starts: 0.7424
Number of communities: 7
Elapsed time: 0 seconds
DimPlot(trA.integrated, group.by = c("orig.ident", "ident"))
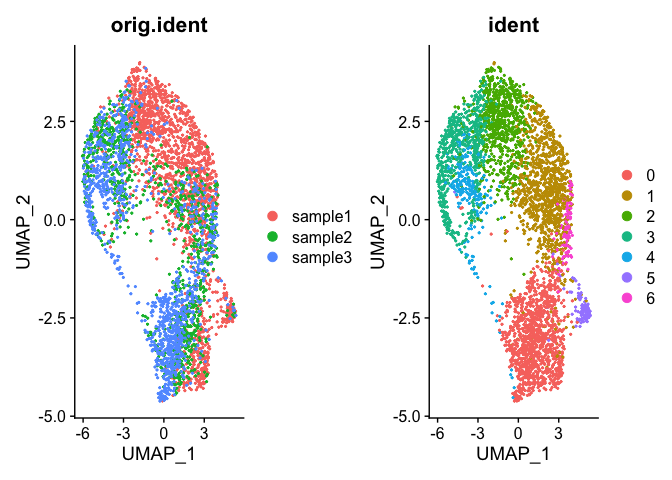 QUESTION
QUESTION
How does this result look different from the result produced in the velocity section?
Setting up monocle3 cell_data_set object using the SueratWrappers
monocle3 uses a cell_data_set object, the as.cell_data_set function from SeuratWrappers can be used to “convert” a Seurat object to Monocle object. Moving the data calculated in Seurat to the appropriate slots in the Monocle object.
For trajectory analysis, ‘partitions’ as well as ‘clusters’ are needed and so the Monocle cluster_cells function must also be performed. Monocle’s clustering technique is more of a community based algorithm and actually uses the uMap plot (sort of) in its routine and partitions are more well separated groups using a statistical test from Alex Wolf et al,
cds <- as.cell_data_set(trA.integrated)
cds <- cluster_cells(cds, resolution=1e-3)
p1 <- plot_cells(cds, color_cells_by = "cluster", show_trajectory_graph = FALSE)
p2 <- plot_cells(cds, color_cells_by = "partition", show_trajectory_graph = FALSE)
wrap_plots(p1, p2)
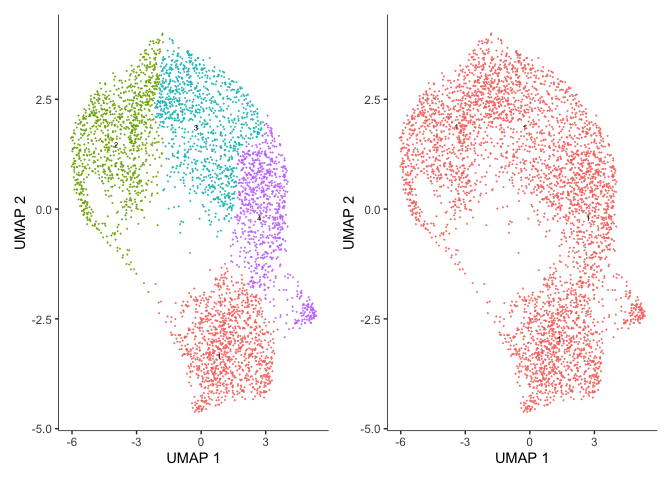
Spend a moment looking at the cell_data_set object and its slots (using slotNames) as well as cluster_cells. Try updating the resolution parameter to generate more clusters (try 1e-5, 1e-3, 1e-1, and 0).
How many clusters are generated at each level?
Subsetting partitions
Because partitions are high level separations of the data (yes we have only 1 here). It may make sense to then perform trajectory analysis on each partition separately. To do this we sould go back to Seurat, subset by partition, then back to a CDS
integrated.sub <- subset(as.Seurat(cds, assay = NULL), monocle3_partitions == 1)
cds <- as.cell_data_set(integrated.sub)
Using existing Monocle 3 cluster membership and partitions
Trajectory analysis
In a data set like this one, cells were not harvested in a time series, but may not have all been at the same developmental stage. Monocle offers trajectory analysis to model the relationships between groups of cells as a trajectory of gene expression changes. The first step in trajectory analysis is the learn_graph() function. This may be time consuming.
cds <- learn_graph(cds, use_partition = TRUE, verbose = FALSE)
After learning the graph, monocle can plot add the trajectory graph to the cell plot.
plot_cells(cds,
color_cells_by = "cluster",
label_groups_by_cluster=FALSE,
label_leaves=FALSE,
label_branch_points=FALSE)
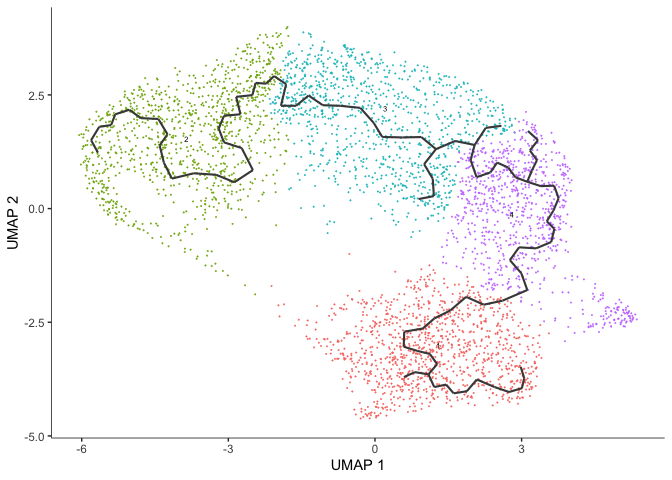
Not all of our trajectories are connected. In fact, only clusters that belong to the same partition are connected by a trajectory.
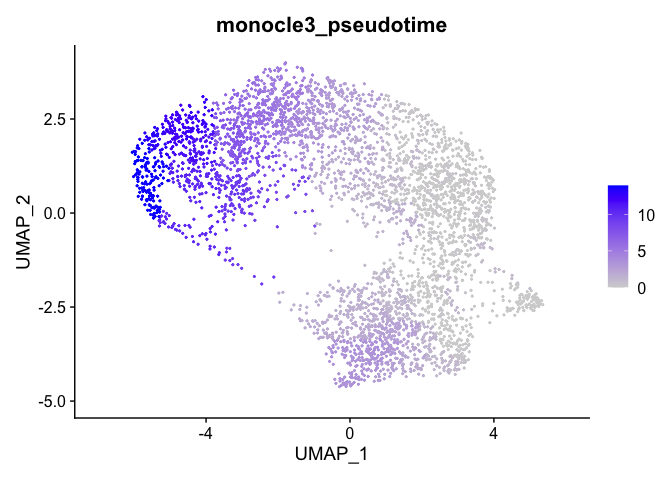
Color cells by pseudotime
We can set the root to any one of our clusters by selecting the cells in that cluster to use as the root in the function order_cells. All cells that cannot be reached from a trajectory with our selected root will be gray, which represents “infinite” pseudotime.
cds <- order_cells(cds, root_cells = colnames(cds[,clusters(cds) == 4]))
plot_cells(cds,
color_cells_by = "pseudotime",
group_cells_by = "cluster",
label_cell_groups = FALSE,
label_groups_by_cluster=FALSE,
label_leaves=FALSE,
label_branch_points=FALSE,
label_roots = FALSE,
trajectory_graph_color = "grey60")
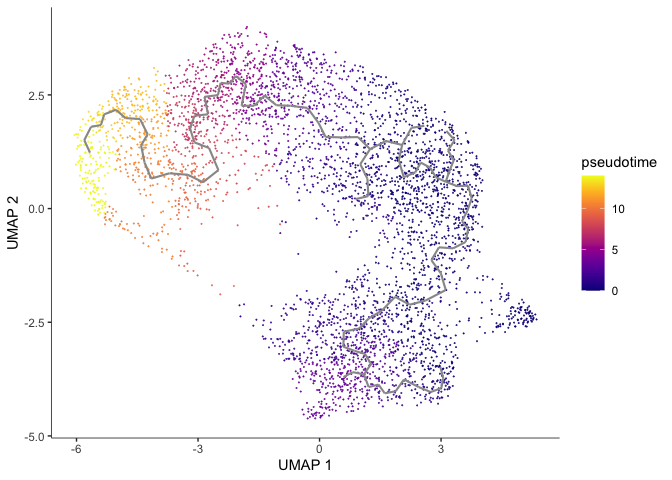
Here the pseudotime trajectory is rooted in cluster 5. This choice was arbitrary. In reality, you would make the decision about where to root your trajectory based upon what you know about your experiment. If, for example, the markers identified with cluster 1 suggest to you that cluster 1 represents the earliest developmental time point, you would likely root your pseudotime trajectory there. Explore what the pseudotime analysis looks like with the root in different clusters. Because we have not set a seed for the random process of clustering, cluster numbers will differ between R sessions.
We can export this data to the Seurat object and visualize
integrated.sub <- as.Seurat(cds, assay = NULL)
FeaturePlot(integrated.sub, "monocle3_pseudotime")
Identify genes that change as a function of pseudotime
Monocle’s graph_test() function detects genes that vary over a trajectory. This may run very slowly. Adjust the number of cores as needed.
cds_graph_test_results <- graph_test(cds,
neighbor_graph = "principal_graph",
cores = 8)
- You may have an issue with this function in newer version of R an rBind Error.
- Can fix this by:
- trace(‘calculateLW’, edit = T, where = asNamespace(“monocle3”))
- find Matrix::rBind and replace with rbind then save.
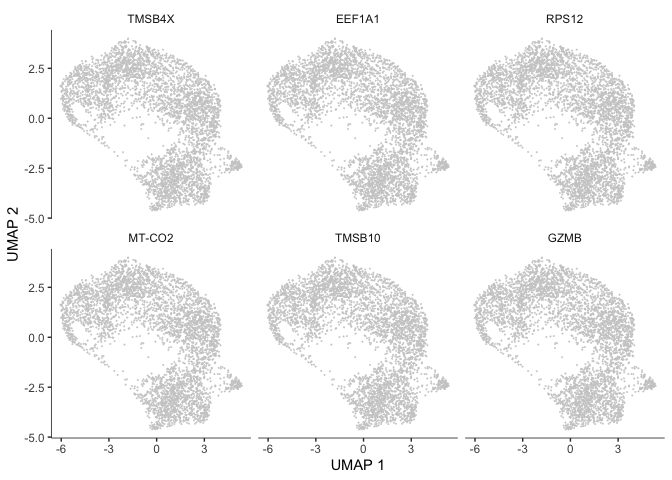
The output of this function is a table. We can look at the expression of some of these genes overlaid on the trajectory plot.
rowData(cds)$gene_short_name <- row.names(rowData(cds))
head(cds_graph_test_results, error=FALSE, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE)
deg_ids <- rownames(subset(cds_graph_test_results[order(cds_graph_test_results$morans_I, decreasing = TRUE),], q_value < 0.05))
plot_cells(cds,
genes=head(deg_ids),
show_trajectory_graph = FALSE,
label_cell_groups = FALSE,
label_leaves = FALSE)
We can also calculate modules of co-expressed genes. By providing the module-finding function with a list of possible resolutions, we are telling Louvain to perform the clustering at each resolution and select the result with the greatest modularity. Modules will only be calculated for genes that vary as a function of pseudotime.
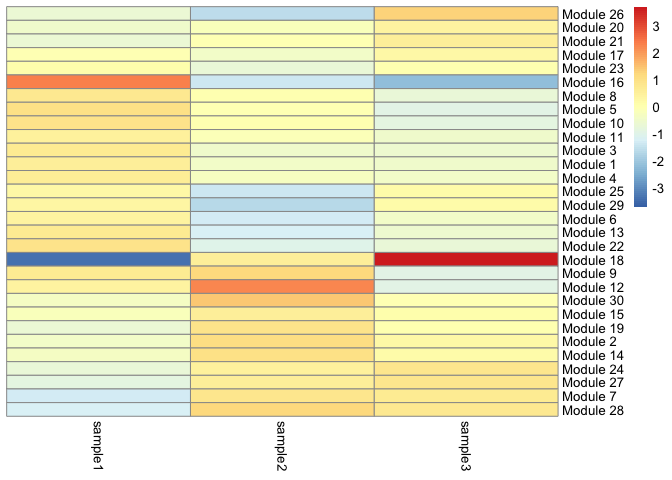
This heatmap displays the association of each gene module with each cell type.
gene_modules <- find_gene_modules(cds[deg_ids,],
resolution=c(10^seq(-6,-1)))
table(gene_modules$module)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
70 70 69 64 60 56 55 54 54 50 49 48 47 45 44 43 40 40 39 39 39 35 32 32 29 29
27 28 29 30
28 27 27 17
cell_groups <- data.frame(cell = row.names(colData(cds)),
cell_group = colData(cds)$orig.ident)
agg_mat <- aggregate_gene_expression(cds,
gene_group_df = gene_modules,
cell_group_df = cell_groups)
dim(agg_mat)
[1] 30 3
row.names(agg_mat) <- paste0("Module ", row.names(agg_mat))
pheatmap::pheatmap(agg_mat,
scale="column",
treeheight_row = 0,
treeheight_col = 0,
clustering_method="ward.D2")
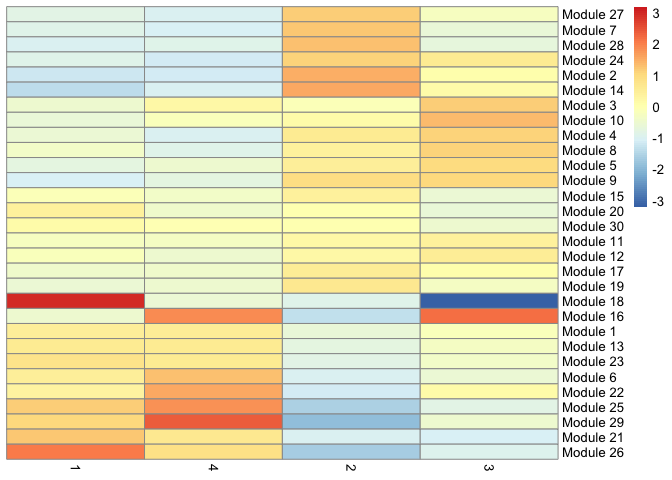
 We can also display the relationship between gene modules and monocle clusters as a heatmap.
We can also display the relationship between gene modules and monocle clusters as a heatmap.
cluster_groups <- data.frame(cell = row.names(colData(cds)),
cluster_group = cds@clusters$UMAP[[2]])
agg_mat2 <- aggregate_gene_expression(cds, gene_modules, cluster_groups)
dim(agg_mat2)
[1] 30 4
row.names(agg_mat2) <- paste0("Module ", row.names(agg_mat2))
pheatmap::pheatmap(agg_mat2,
scale="column",
treeheight_row = 0,
treeheight_col = 0,
clustering_method="ward.D2")
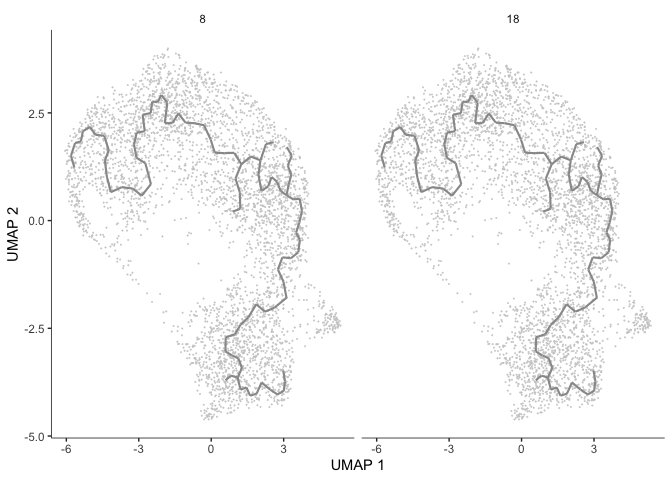
gm <- gene_modules[which(gene_modules$module %in% c(8, 18)),]
plot_cells(cds,
genes=gm,
label_cell_groups=FALSE,
show_trajectory_graph=TRUE,
label_branch_points = FALSE,
label_roots = FALSE,
label_leaves = FALSE,
trajectory_graph_color = "grey60")
Warning: `guides(
= FALSE)` is deprecated. Please use `guides( =
"none")` instead.
</div>
# R session information
```r
sessionInfo()
```
R version 4.1.0 (2021-05-18)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Big Sur 10.16
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.1/Resources/lib/libRblas.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.1/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats4 parallel stats graphics grDevices utils datasets
[8] methods base
other attached packages:
[1] patchwork_1.1.1 SeuratWrappers_0.3.0
[3] SeuratObject_4.0.2 Seurat_4.0.3
[5] monocle3_1.0.0 SingleCellExperiment_1.14.1
[7] SummarizedExperiment_1.22.0 GenomicRanges_1.44.0
[9] GenomeInfoDb_1.28.1 IRanges_2.26.0
[11] S4Vectors_0.30.0 MatrixGenerics_1.4.2
[13] matrixStats_0.60.0 Biobase_2.52.0
[15] BiocGenerics_0.38.0
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] plyr_1.8.6 igraph_1.2.6 lazyeval_0.2.2
[4] sp_1.4-5 splines_4.1.0 listenv_0.8.0
[7] scattermore_0.7 ggplot2_3.3.5 digest_0.6.27
[10] htmltools_0.5.1.1 viridis_0.6.1 gdata_2.18.0
[13] fansi_0.5.0 magrittr_2.0.1 tensor_1.5
[16] cluster_2.1.2 ROCR_1.0-11 remotes_2.4.0
[19] globals_0.14.0 gmodels_2.18.1 R.utils_2.10.1
[22] spatstat.sparse_2.0-0 colorspace_2.0-2 ggrepel_0.9.1
[25] xfun_0.25 dplyr_1.0.7 crayon_1.4.1
[28] RCurl_1.98-1.4 jsonlite_1.7.2 spatstat.data_2.1-0
[31] survival_3.2-12 zoo_1.8-9 glue_1.4.2
[34] polyclip_1.10-0 gtable_0.3.0 zlibbioc_1.38.0
[37] XVector_0.32.0 leiden_0.3.9 DelayedArray_0.18.0
[40] future.apply_1.8.1 abind_1.4-5 scales_1.1.1
[43] pheatmap_1.0.12 DBI_1.1.1 miniUI_0.1.1.1
[46] Rcpp_1.0.7 spData_0.3.10 viridisLite_0.4.0
[49] xtable_1.8-4 units_0.7-2 reticulate_1.20
[52] spatstat.core_2.3-0 spdep_1.1-8 proxy_0.4-26
[55] bit_4.0.4 rsvd_1.0.5 htmlwidgets_1.5.3
[58] httr_1.4.2 RColorBrewer_1.1-2 ellipsis_0.3.2
[61] ica_1.0-2 farver_2.1.0 pkgconfig_2.0.3
[64] R.methodsS3_1.8.1 sass_0.4.0 uwot_0.1.10
[67] deldir_0.2-10 utf8_1.2.2 tidyselect_1.1.1
[70] labeling_0.4.2 rlang_0.4.11 reshape2_1.4.4
[73] later_1.3.0 pbmcapply_1.5.0 munsell_0.5.0
[76] tools_4.1.0 generics_0.1.0 ggridges_0.5.3
[79] evaluate_0.14 stringr_1.4.0 fastmap_1.1.0
[82] yaml_2.2.1 goftest_1.2-2 knitr_1.33
[85] bit64_4.0.5 fitdistrplus_1.1-5 purrr_0.3.4
[88] RANN_2.6.1 pbapply_1.4-3 future_1.21.0
[91] nlme_3.1-152 mime_0.11 slam_0.1-48
[94] grr_0.9.5 R.oo_1.24.0 hdf5r_1.3.3
[97] compiler_4.1.0 plotly_4.9.4.1 png_0.1-7
[100] e1071_1.7-8 spatstat.utils_2.2-0 tibble_3.1.3
[103] bslib_0.2.5.1 stringi_1.7.3 highr_0.9
[106] RSpectra_0.16-0 lattice_0.20-44 Matrix_1.3-4
[109] classInt_0.4-3 vctrs_0.3.8 LearnBayes_2.15.1
[112] pillar_1.6.2 lifecycle_1.0.0 BiocManager_1.30.16
[115] spatstat.geom_2.2-2 lmtest_0.9-38 jquerylib_0.1.4
[118] RcppAnnoy_0.0.19 data.table_1.14.0 cowplot_1.1.1
[121] bitops_1.0-7 irlba_2.3.3 Matrix.utils_0.9.8
[124] raster_3.4-13 httpuv_1.6.2 R6_2.5.1
[127] promises_1.2.0.1 KernSmooth_2.23-20 gridExtra_2.3
[130] parallelly_1.27.0 codetools_0.2-18 gtools_3.9.2
[133] boot_1.3-28 MASS_7.3-54 assertthat_0.2.1
[136] leidenbase_0.1.3 sctransform_0.3.2 GenomeInfoDbData_1.2.6
[139] expm_0.999-6 mgcv_1.8-36 grid_4.1.0
[142] rpart_4.1-15 coda_0.19-4 class_7.3-19
[145] tidyr_1.1.3 rmarkdown_2.10 Rtsne_0.15
[148] sf_1.0-2 shiny_1.6.0
 QUESTION
QUESTION




 We can also display the relationship between gene modules and monocle clusters as a heatmap.
We can also display the relationship between gene modules and monocle clusters as a heatmap.
