Differential Gene Expression Analysis in R
Differential Gene Expression (DGE) between conditions is determined from count data
Generally speaking differential expression analysis is performed in a very similar manner to DNA microarrays, once normalization and transformations have been performed.
A lot of RNA-seq analysis has been done in R and so there are many packages available to analyze and view this data. Two of the most commonly used are:
DESeq2, developed by Simon Anders (also created htseq) in Wolfgang Huber’s group at EMBL
edgeR and Voom (extension to Limma [microarrays] for RNA-seq), developed out of Gordon Smyth’s group from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research in Australia
http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/BiocViews.html#___RNASeq
Differential Expression Analysis with Limma-Voom
limma is an R package that was originally developed for differential expression (DE) analysis of gene expression microarray data.
voom is a function in the limma package that transforms RNA-Seq data for use with limma.
Together they allow fast, flexible, and powerful analyses of RNA-Seq data. Limma-voom is our tool of choice for DE analyses because it:
Allows for incredibly flexible model specification (you can include multiple categorical and continuous variables, allowing incorporation of almost any kind of metadata).
Based on simulation studies, maintains the false discovery rate at or below the nominal rate, unlike some other packages.
Empirical Bayes smoothing of gene-wise standard deviations provides increased power.
Basic Steps of Differential Gene Expression
Read count data and annotation into R and preprocessing.
Calculate normalization factors (sample-specific adjustments)
Filter genes (uninteresting genes, e.g. unexpressed)
Account for expression-dependent variability by transformation, weighting, or modeling
Fitting a linear model
Perform statistical comparisons of interest (using contrasts)
Adjust for multiple testing, Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) or q-value
Check results for confidence
Attach annotation if available and write tables
1. Read in the counts table and create our DGEList
counts <- read.delim ( "rnaseq_workshop_counts.txt" , row.names = 1 )
head ( counts )
mouse_110_WT_C mouse_110_WT_NC mouse_148_WT_C
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0 0
mouse_148_WT_NC mouse_158_WT_C mouse_158_WT_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0 0
mouse_183_KOMIR150_C mouse_183_KOMIR150_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0
mouse_198_KOMIR150_C mouse_198_KOMIR150_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0
mouse_206_KOMIR150_C mouse_206_KOMIR150_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0
mouse_2670_KOTet3_C mouse_2670_KOTet3_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0
mouse_7530_KOTet3_C mouse_7530_KOTet3_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0
mouse_7531_KOTet3_C mouse_7532_WT_NC mouse_H510_WT_C
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0 0
mouse_H510_WT_NC mouse_H514_WT_C mouse_H514_WT_NC
ENSMUSG00000102693.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000064842.3 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000051951.6 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000102851.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000103377.2 0 0 0
ENSMUSG00000104017.2 0 0 0
Create Differential Gene Expression List Object (DGEList) object
A DGEList is an object in the package edgeR for storing count data, normalization factors, and other information
1a. Read in Annotation
anno <- read.delim ( "ensembl_mm_106.tsv" , as.is = T )
dim ( anno )
[1] 55414 11
Gene.stable.ID Gene.stable.ID.version Gene.name Gene.type
1 ENSMUSG00000064336 ENSMUSG00000064336.1 mt-Tf Mt_tRNA
2 ENSMUSG00000064337 ENSMUSG00000064337.1 mt-Rnr1 Mt_rRNA
3 ENSMUSG00000064338 ENSMUSG00000064338.1 mt-Tv Mt_tRNA
4 ENSMUSG00000064339 ENSMUSG00000064339.1 mt-Rnr2 Mt_rRNA
5 ENSMUSG00000064340 ENSMUSG00000064340.1 mt-Tl1 Mt_tRNA
6 ENSMUSG00000064341 ENSMUSG00000064341.1 mt-Nd1 protein_coding
Transcript.count Gene.start..bp. Gene.end..bp. Strand
1 1 1 68 1
2 1 70 1024 1
3 1 1025 1093 1
4 1 1094 2675 1
5 1 2676 2750 1
6 1 2751 3707 1
Gene.description
1 mitochondrially encoded tRNA phenylalanine [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:102487]
2 mitochondrially encoded 12S rRNA [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:102493]
3 mitochondrially encoded tRNA valine [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:102472]
4 mitochondrially encoded 16S rRNA [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:102492]
5 mitochondrially encoded tRNA leucine 1 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:102482]
6 mitochondrially encoded NADH dehydrogenase 1 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:101787]
Gene...GC.content Chromosome.scaffold.name
1 30.88 MT
2 35.81 MT
3 39.13 MT
4 35.40 MT
5 44.00 MT
6 37.62 MT
Gene.stable.ID Gene.stable.ID.version Gene.name
55409 ENSMUSG00000044103 ENSMUSG00000044103.5 Il36g
55410 ENSMUSG00000026984 ENSMUSG00000026984.5 Il36a
55411 ENSMUSG00000104173 ENSMUSG00000104173.2 Gm37703
55412 ENSMUSG00000083172 ENSMUSG00000083172.2 Gm13409
55413 ENSMUSG00000026983 ENSMUSG00000026983.11 Il36rn
55414 ENSMUSG00000046845 ENSMUSG00000046845.2 Il1f10
Gene.type Transcript.count Gene.start..bp. Gene.end..bp.
55409 protein_coding 1 24076488 24083580
55410 protein_coding 2 24105430 24115714
55411 TEC 1 24121880 24123663
55412 unprocessed_pseudogene 1 24151842 24156350
55413 protein_coding 7 24166966 24173438
55414 protein_coding 1 24181208 24183832
Strand
55409 1
55410 1
55411 1
55412 -1
55413 1
55414 1
Gene.description
55409 interleukin 36G [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:2449929]
55410 interleukin 36A [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:1859324]
55411 predicted gene, 37703 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:5610931]
55412 predicted gene 13409 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:3651609]
55413 interleukin 36 receptor antagonist [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:1859325]
55414 interleukin 1 family, member 10 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:2652548]
Gene...GC.content Chromosome.scaffold.name
55409 42.00 2
55410 39.61 2
55411 40.08 2
55412 38.30 2
55413 45.43 2
55414 46.36 2
any ( duplicated ( anno $ Gene.stable.ID ))
[1] FALSE
1b. Derive experiment metadata from the sample names
Our experiment has two factors, genotype (“WT”, “KOMIR150”, or “KOTet3”) and cell type (“C” or “NC”).
The sample names are “mouse” followed by an animal identifier, followed by the genotype, followed by the cell type.
sample_names <- colnames ( counts )
metadata <- as.data.frame ( strsplit2 ( sample_names , c ( "_" ))[, 2 : 4 ], row.names = sample_names )
colnames ( metadata ) <- c ( "mouse" , "genotype" , "cell_type" )
Create a new variable “group” that combines genotype and cell type.
metadata $ group <- interaction ( metadata $ genotype , metadata $ cell_type )
table ( metadata $ group )
KOMIR150.C KOTet3.C WT.C KOMIR150.NC KOTet3.NC WT.NC
3 3 5 3 2 6
110 148 158 183 198 206 2670 7530 7531 7532 H510 H514
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2
Note: you can also enter group information manually, or read it in from an external file. If you do this, it is $VERY, VERY, VERY$ important that you make sure the metadata is in the same order as the column names of the counts table.
Quiz 1
Submit Quiz
2. Preprocessing and Normalization factors
In differential expression analysis, only sample-specific effects need to be normalized, we are NOT concerned with comparisons and quantification of absolute expression.
Sequence depth – is a sample specific effect and needs to be adjusted for.
RNA composition - finding a set of scaling factors for the library sizes that minimize the log-fold changes between the samples for most genes (edgeR uses a trimmed mean of M-values between each pair of sample)
GC content – is NOT sample-specific (except when it is)
Gene Length – is NOT sample-specific (except when it is)
In edgeR/limma, you calculate normalization factors to scale the raw library sizes (number of reads) using the function calcNormFactors, which by default uses TMM (weighted trimmed means of M values to the reference). Assumes most genes are not DE.
Proposed by Robinson and Oshlack (2010).
d0 <- calcNormFactors ( d0 )
d0 $ samples
group lib.size norm.factors
mouse_110_WT_C 1 2354047 1.0377120
mouse_110_WT_NC 1 2855542 0.9883050
mouse_148_WT_C 1 2832974 1.0117329
mouse_148_WT_NC 1 2629970 0.9817121
mouse_158_WT_C 1 2993210 1.0017491
mouse_158_WT_NC 1 2673435 0.9629221
mouse_183_KOMIR150_C 1 2552200 1.0277658
mouse_183_KOMIR150_NC 1 1873049 1.0135566
mouse_198_KOMIR150_C 1 2859228 1.0102789
mouse_198_KOMIR150_NC 1 2938965 0.9864590
mouse_206_KOMIR150_C 1 1399381 0.9850821
mouse_206_KOMIR150_NC 1 959879 0.9915571
mouse_2670_KOTet3_C 1 2923622 0.9944173
mouse_2670_KOTet3_NC 1 2956486 0.9780692
mouse_7530_KOTet3_C 1 2631467 1.0172313
mouse_7530_KOTet3_NC 1 2903155 0.9615916
mouse_7531_KOTet3_C 1 2682282 1.0227600
mouse_7532_WT_NC 1 2730871 1.0052820
mouse_H510_WT_C 1 2601596 1.0201380
mouse_H510_WT_NC 1 2852724 1.0256272
mouse_H514_WT_C 1 2316653 0.9901225
mouse_H514_WT_NC 1 2666148 0.9904483
Note: calcNormFactors doesn’t normalize the data, it just calculates normalization factors for use downstream.
3. Filtering genes
We filter genes based on non-experimental factors to reduce the number of genes/tests being conducted and therefor do not have to be accounted for in our transformation or multiple testing correction. Commonly we try to remove genes that are either a) unexpressed, or b) unchanging (low-variability).
Common filters include:
to remove genes with a max value (X) of less then Y.
to remove genes that are less than X normalized read counts (cpm) across a certain number of samples. Ex: rowSums(cpms <=1) < 3 , require at least 1 cpm in at least 3 samples to keep.
A less used filter is for genes with minimum variance across all samples, so if a gene isn’t changing (constant expression) its inherently not interesting therefor no need to test.
We will use the built in function filterByExpr() to filter low-expressed genes. filterByExpr uses the experimental design to determine how many samples a gene needs to be expressed in to stay. Importantly, once this number of samples has been determined, the group information is not used in filtering.
Using filterByExpr requires specifying the model we will use to analysis our data.
The model you use will change for every experiment, and this step should be given the most time and attention.*
We use a model that includes group and (in order to account for the paired design) mouse.
group <- metadata $ group
mouse <- metadata $ mouse
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ 0 + group + mouse )
head ( mm )
groupKOMIR150.C groupKOTet3.C groupWT.C groupKOMIR150.NC groupKOTet3.NC
1 0 0 1 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 1 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 1 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 0
groupWT.NC mouse148 mouse158 mouse183 mouse198 mouse206 mouse2670 mouse7530
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
6 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
mouse7531 mouse7532 mouseH510 mouseH514
1 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0
keep <- filterByExpr ( d0 , mm )
sum ( keep ) # number of genes retained
[1] 11430
“Low-expressed” depends on the dataset and can be subjective.
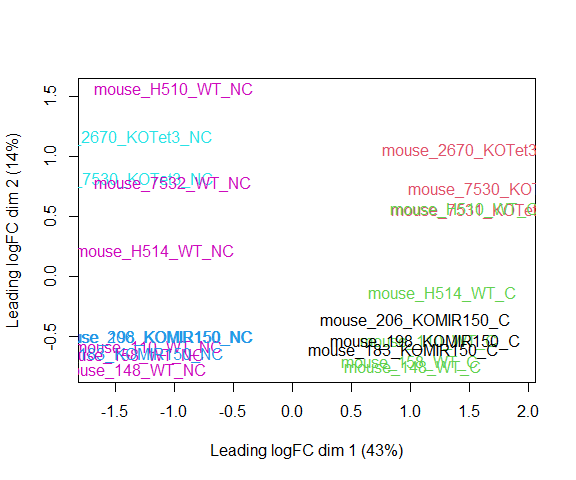
Visualizing your data with a Multidimensional scaling (MDS) plot.
plotMDS ( d , col = as.numeric ( metadata $ group ), cex = 1 )
The MDS plot tells you A LOT about what to expect from your experiment.
3a. Extracting “normalized” expression table
RPKM vs. FPKM vs. CPM and Model Based
RPKM - Reads per kilobase per million mapped reads
FPKM - Fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads
logCPM – log Counts per million [ good for producing MDS plots, estimate of normalized values in model based ]
Model based - original read counts are not themselves transformed, but rather correction factors are used in the DE model itself.
We use the cpm function with log=TRUE to obtain log-transformed normalized expression data. On the log scale, the data has less mean-dependent variability and is more suitable for plotting.
logcpm <- cpm ( d , prior.count = 2 , log = TRUE )
write.table ( logcpm , "rnaseq_workshop_normalized_counts.txt" , sep = "\t" , quote = F )
Quiz 2
Submit Quiz
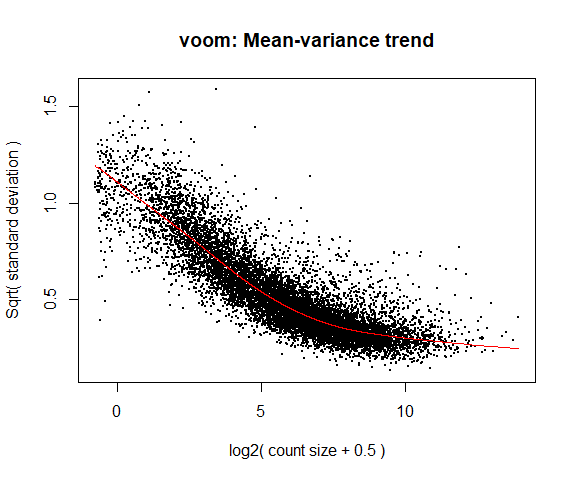
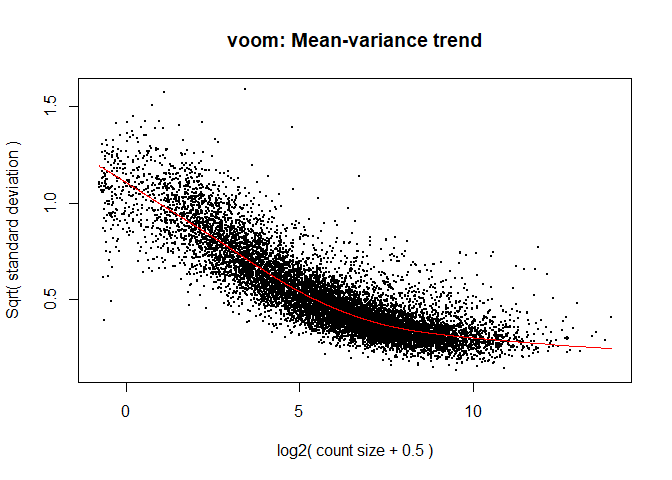
4a. Voom
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = T )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
What is voom doing?
Counts are transformed to log2 counts per million reads (CPM), where “per million reads” is defined based on the normalization factors we calculated earlier.
A linear model is fitted to the log2 CPM for each gene, and the residuals are calculated.
A smoothed curve is fitted to the sqrt(residual standard deviation) by average expression.
(see red line in plot above)
The smoothed curve is used to obtain weights for each gene and sample that are passed into limma along with the log2 CPMs.
More details at “voom: precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts ”
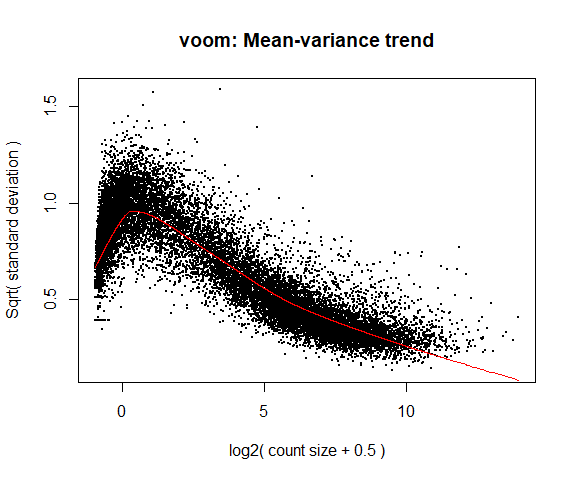
If your voom plot looks like the below (performed on the raw data), you might want to filter more:
tmp <- voom ( d0 , mm , plot = T )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 55414 probe(s)
5. Fitting linear models in limma
lmFit fits a linear model using weighted least squares for each gene:
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
groupKOMIR150.C groupKOTet3.C groupWT.C groupKOMIR150.NC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 4.863263 5.011676 4.759326 5.109324
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 5.135887 5.636828 5.519602 5.260182
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 5.887608 5.647359 5.773644 5.939362
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 5.259696 5.383275 5.420424 5.079821
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 6.523165 6.660415 6.541454 6.341045
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 2.281048 3.474808 1.883502 2.426840
groupKOTet3.NC groupWT.NC mouse148 mouse158
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 4.739022 4.624170 0.23192176 0.16747528
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 5.601852 5.356630 -0.03872025 0.04806943
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 5.812784 5.781199 0.05756464 0.04179097
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 4.859325 5.150285 -0.16351899 -0.22593717
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 6.752318 6.289800 -0.10198768 -0.02426407
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 3.808701 2.087661 -0.10839188 0.11945290
mouse183 mouse198 mouse206 mouse2670 mouse7530
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 -0.4528993 -0.10127318 NA -0.04037166 -0.009073243
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.3685759 0.41175400 NA 0.06371351 -0.116244875
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 -0.2529610 -0.00841256 NA 0.17471195 0.200158401
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.3302039 0.06166284 NA 0.13088790 0.391433836
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 -0.1209212 0.12443747 NA -0.09360513 -0.137224529
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 -0.3786011 0.15564447 NA -1.09960890 -0.199717680
mouse7531 mouse7532 mouseH510 mouseH514
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 NA 0.19499278 0.16951088 0.15722271
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 NA 0.25787054 0.10923179 0.22799700
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 NA 0.06104751 0.04599131 -0.03185153
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 NA -0.29436437 -0.03879120 -0.15132577
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 NA 0.18101608 0.01135225 -0.12996434
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 NA 1.89832058 1.25166060 1.45045597
Comparisons between groups (log fold-changes) are obtained as contrasts of these fitted linear models:
6. Specify which groups to compare using contrasts:
Comparison between cell types for genotype WT.
contr <- makeContrasts ( groupWT.C - groupWT.NC , levels = colnames ( coef ( fit )))
contr
Contrasts
Levels groupWT.C - groupWT.NC
groupKOMIR150.C 0
groupKOTet3.C 0
groupWT.C 1
groupKOMIR150.NC 0
groupKOTet3.NC 0
groupWT.NC -1
mouse148 0
mouse158 0
mouse183 0
mouse198 0
mouse206 0
mouse2670 0
mouse7530 0
mouse7531 0
mouse7532 0
mouseH510 0
mouseH514 0
6a. Estimate contrast for each gene
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , contr )
The variance characteristics of low expressed genes are different from high expressed genes, if treated the same, the effect is to over represent low expressed genes in the DE list. This is corrected for by the log transformation and voom. However, some genes will have increased or decreased variance that is not a result of low expression, but due to other random factors. We are going to run empirical Bayes to adjust the variance of these genes.
Empirical Bayes smoothing of standard errors (shifts standard errors that are much larger or smaller than those from other genes towards the average standard error) (see “Linear Models and Empirical Bayes Methods for Assessing Differential Expression in Microarray Experiments ”
6b. Apply EBayes
7. Multiple Testing Adjustment
The TopTable. Adjust for multiple testing using method of Benjamini & Hochberg (BH), or its ‘alias’ fdr. “Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing .
here n=Inf says to produce the topTable for all genes.
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , adjust.method = "BH" , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
Multiple Testing Correction
Simply a must! Best choices are:
FDR (false discovery rate), such as Benjamini-Hochberg (1995).Qvalue - Storey (2002)
The FDR (or qvalue) is a statement about the list and is no longer about the gene (pvalue). So a FDR of 0.05, says you expect 5% false positives among the list of genes with an FDR of 0.05 or less.
The statement “Statistically significantly different” means FDR of 0.05 or less.
7a. How many DE genes are there (false discovery rate corrected)?
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 ))
[1] 5629
8. Check your results for confidence.
You’ve conducted an experiment, you’ve seen a phenotype. Now check which genes are most differentially expressed (show the top 50)? Look up these top genes, their description and ensure they relate to your experiment/phenotype.
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 -2.487719 7.859085 -45.36099 4.383027e-19 5.009800e-15
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 4.552564 6.190761 40.11910 3.423886e-18 1.503259e-14
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 2.164336 9.879972 39.78025 3.945562e-18 1.503259e-14
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 -4.121437 6.993895 -34.01395 5.384455e-17 1.538608e-13
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 -1.899178 8.112819 -33.27597 7.758438e-17 1.617246e-13
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 -2.676304 8.356926 -33.09644 8.489480e-17 1.617246e-13
ENSMUSG00000024164.16 1.800345 9.861523 32.30710 1.268544e-16 1.877277e-13
ENSMUSG00000037820.16 -4.167030 7.117017 -32.23889 1.313930e-16 1.877277e-13
ENSMUSG00000026193.16 4.807150 10.143888 31.56222 1.869556e-16 2.374336e-13
ENSMUSG00000038807.20 -1.562385 9.003435 -30.13553 4.030599e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000048498.8 -5.792618 6.490525 -29.99180 4.363377e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000030342.9 -3.676052 6.037901 -29.72488 5.060942e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000030413.8 -2.607215 6.640096 -29.59990 5.427287e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000028885.9 -2.352285 7.043042 -29.59920 5.429402e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000021614.17 6.000776 5.427433 29.51572 5.689750e-16 4.335589e-13
ENSMUSG00000051177.17 3.186136 4.985785 29.30344 6.413131e-16 4.581381e-13
ENSMUSG00000027215.14 -2.570287 6.889976 -29.00858 7.583544e-16 4.938916e-13
ENSMUSG00000018168.9 -3.877965 5.456099 -28.93985 7.887579e-16 4.938916e-13
ENSMUSG00000029254.17 -2.453517 6.686492 -28.86998 8.209922e-16 4.938916e-13
ENSMUSG00000020437.13 -1.227240 10.305628 -28.68992 9.106557e-16 5.060930e-13
ENSMUSG00000039959.14 -1.483730 8.932030 -28.65386 9.298296e-16 5.060930e-13
ENSMUSG00000037185.10 -1.536915 9.479745 -28.19371 1.215712e-15 6.296814e-13
ENSMUSG00000038147.15 1.689781 7.138335 28.12332 1.267076e-15 6.296814e-13
ENSMUSG00000020108.5 -2.051154 6.943149 -27.97858 1.380041e-15 6.572448e-13
ENSMUSG00000020212.15 -2.163284 6.773920 -27.89693 1.448423e-15 6.622189e-13
ENSMUSG00000023827.9 -2.143751 6.405974 -27.80537 1.529400e-15 6.723477e-13
ENSMUSG00000022584.15 4.737856 6.735796 27.66914 1.658850e-15 7.022466e-13
ENSMUSG00000023809.11 -3.192699 4.823849 -27.49195 1.844820e-15 7.530818e-13
ENSMUSG00000020272.9 -1.299449 10.443529 -27.16976 2.241822e-15 8.633658e-13
ENSMUSG00000020387.16 -4.934650 4.326562 -27.11322 2.320355e-15 8.633658e-13
ENSMUSG00000018001.19 -2.613949 7.171269 -27.09828 2.341587e-15 8.633658e-13
ENSMUSG00000021728.9 1.661441 8.386923 26.95813 2.551093e-15 9.112186e-13
ENSMUSG00000008496.20 -1.485361 9.416862 -26.49805 3.390083e-15 1.174201e-12
ENSMUSG00000035493.11 1.922719 9.747251 26.23559 3.995526e-15 1.343202e-12
ENSMUSG00000026923.16 2.014555 6.623886 25.95612 4.767785e-15 1.526455e-12
ENSMUSG00000039109.18 4.740467 8.315280 25.94299 4.807732e-15 1.526455e-12
ENSMUSG00000042700.17 -1.813816 6.083974 -25.80378 5.253884e-15 1.623024e-12
ENSMUSG00000051457.8 -2.264000 9.813220 -25.60064 5.985169e-15 1.800276e-12
ENSMUSG00000043263.14 1.784129 7.845866 25.40127 6.808339e-15 1.947848e-12
ENSMUSG00000029287.15 -3.782709 5.404369 -25.39940 6.816615e-15 1.947848e-12
ENSMUSG00000044783.17 -1.728670 7.013074 -25.36125 6.987571e-15 1.947998e-12
ENSMUSG00000025701.13 -2.754362 5.339213 -25.24728 7.525826e-15 2.048100e-12
ENSMUSG00000050335.18 1.111875 8.961147 25.03993 8.620692e-15 2.291500e-12
ENSMUSG00000033705.18 1.697567 7.148728 24.98003 8.967477e-15 2.329506e-12
ENSMUSG00000022818.14 -1.748293 6.777005 -24.74549 1.047401e-14 2.645144e-12
ENSMUSG00000027435.9 3.036123 6.718151 24.72110 1.064537e-14 2.645144e-12
ENSMUSG00000016496.8 -3.559684 6.399550 -24.51906 1.218433e-14 2.963125e-12
ENSMUSG00000005800.4 5.749952 4.124806 24.24865 1.462200e-14 3.481863e-12
ENSMUSG00000020340.17 -2.254179 8.644957 -24.19352 1.517948e-14 3.540845e-12
ENSMUSG00000034731.12 -1.747589 6.597146 -24.08389 1.635596e-14 3.738972e-12
B
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 33.99666
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 31.51334
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 31.90164
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 29.22222
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 28.93065
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 28.83896
ENSMUSG00000024164.16 28.38196
ENSMUSG00000037820.16 28.32938
ENSMUSG00000026193.16 27.96362
ENSMUSG00000038807.20 27.23661
ENSMUSG00000048498.8 26.84866
ENSMUSG00000030342.9 26.91147
ENSMUSG00000030413.8 26.98685
ENSMUSG00000028885.9 26.98913
ENSMUSG00000021614.17 25.71991
ENSMUSG00000051177.17 26.40008
ENSMUSG00000027215.14 26.65346
ENSMUSG00000018168.9 26.43153
ENSMUSG00000029254.17 26.57415
ENSMUSG00000020437.13 26.32075
ENSMUSG00000039959.14 26.37857
ENSMUSG00000037185.10 26.07971
ENSMUSG00000038147.15 26.13767
ENSMUSG00000020108.5 26.04068
ENSMUSG00000020212.15 26.01172
ENSMUSG00000023827.9 25.95162
ENSMUSG00000022584.15 25.85530
ENSMUSG00000023809.11 25.39377
ENSMUSG00000020272.9 25.37937
ENSMUSG00000020387.16 24.09795
ENSMUSG00000018001.19 25.52150
ENSMUSG00000021728.9 25.38037
ENSMUSG00000008496.20 25.02213
ENSMUSG00000035493.11 24.84152
ENSMUSG00000026923.16 24.81325
ENSMUSG00000039109.18 24.75216
ENSMUSG00000042700.17 24.72275
ENSMUSG00000051457.8 24.40923
ENSMUSG00000043263.14 24.39431
ENSMUSG00000029287.15 24.37852
ENSMUSG00000044783.17 24.42201
ENSMUSG00000025701.13 24.28156
ENSMUSG00000050335.18 24.09199
ENSMUSG00000033705.18 24.15264
ENSMUSG00000022818.14 24.01949
ENSMUSG00000027435.9 24.02174
ENSMUSG00000016496.8 23.87710
ENSMUSG00000005800.4 21.81886
ENSMUSG00000020340.17 23.53586
ENSMUSG00000034731.12 23.57744
Columns are
logFC: log2 fold change of WT.C/WT.NC
AveExpr: Average expression across all samples, in log2 CPM
t: logFC divided by its standard error
P.Value: Raw p-value (based on t) from test that logFC differs from 0
adj.P.Val: Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate adjusted p-value
B: log-odds that gene is DE (arguably less useful than the other columns)
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 has higher expression at WT NC than at WT C (logFC is negative). ENSMUSG00000026193.16 has higher expression at WT C than at WT NC (logFC is positive).
In the paper, the authors specify that NC cells were identified by low expression of Ly6C (which is now called Ly6c1 or ENSMUSG00000079018.11). Is this gene differentially expressed?
top.table [ "ENSMUSG00000079018.11" ,]
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val B
NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
d0 $ counts [ "ENSMUSG00000079018.11" ,]
mouse_110_WT_C mouse_110_WT_NC mouse_148_WT_C
2 0 2
mouse_148_WT_NC mouse_158_WT_C mouse_158_WT_NC
0 2 0
mouse_183_KOMIR150_C mouse_183_KOMIR150_NC mouse_198_KOMIR150_C
1 0 1
mouse_198_KOMIR150_NC mouse_206_KOMIR150_C mouse_206_KOMIR150_NC
0 1 0
mouse_2670_KOTet3_C mouse_2670_KOTet3_NC mouse_7530_KOTet3_C
2 0 2
mouse_7530_KOTet3_NC mouse_7531_KOTet3_C mouse_7532_WT_NC
0 1 0
mouse_H510_WT_C mouse_H510_WT_NC mouse_H514_WT_C
1 0 2
mouse_H514_WT_NC
0
Ly6c1 was removed from our data by the filtering step, because the maximum counts for the gene did not exceed 2.
9. Write top.table to a file, adding in cpms and annotation
top.table $ Gene <- rownames ( top.table )
top.table <- top.table [, c ( "Gene" , names ( top.table )[ 1 : 6 ])]
top.table <- data.frame ( top.table , anno [ match ( top.table $ Gene , anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ),], logcpm [ match ( top.table $ Gene , rownames ( logcpm )),])
head ( top.table )
Gene logFC AveExpr t
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 ENSMUSG00000020608.8 -2.487719 7.859085 -45.36099
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 ENSMUSG00000052212.7 4.552564 6.190761 40.11910
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 ENSMUSG00000049103.15 2.164336 9.879972 39.78025
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 ENSMUSG00000030203.18 -4.121437 6.993895 -34.01395
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 ENSMUSG00000027508.16 -1.899178 8.112819 -33.27597
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 ENSMUSG00000021990.17 -2.676304 8.356926 -33.09644
P.Value adj.P.Val B Gene.stable.ID
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 4.383027e-19 5.009800e-15 33.99666 ENSMUSG00000020608
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 3.423886e-18 1.503259e-14 31.51334 ENSMUSG00000052212
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 3.945562e-18 1.503259e-14 31.90164 ENSMUSG00000049103
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 5.384455e-17 1.538608e-13 29.22222 ENSMUSG00000030203
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 7.758438e-17 1.617246e-13 28.93065 ENSMUSG00000027508
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 8.489480e-17 1.617246e-13 28.83896 ENSMUSG00000021990
Gene.stable.ID.version Gene.name Gene.type
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 ENSMUSG00000020608.8 Smc6 protein_coding
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 ENSMUSG00000052212.7 Cd177 protein_coding
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 ENSMUSG00000049103.15 Ccr2 protein_coding
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 ENSMUSG00000030203.18 Dusp16 protein_coding
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 ENSMUSG00000027508.16 Pag1 protein_coding
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 ENSMUSG00000021990.17 Spata13 protein_coding
Transcript.count Gene.start..bp. Gene.end..bp. Strand
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 12 11315887 11369786 1
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 2 24443408 24459736 -1
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 4 123901987 123913594 1
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 7 134692431 134769588 -1
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 5 9752539 9898739 -1
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9 60871450 61002005 1
Gene.description
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 structural maintenance of chromosomes 6 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:1914491]
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 CD177 antigen [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:1916141]
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:106185]
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 dual specificity phosphatase 16 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:1917936]
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid microdomains 1 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:2443160]
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 spermatogenesis associated 13 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:104838]
Gene...GC.content Chromosome.scaffold.name mouse_110_WT_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 38.40 12 6.623815
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 52.26 7 8.612183
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 38.86 9 10.897845
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 41.74 6 4.995235
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 44.66 3 7.178698
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 47.38 14 6.968425
mouse_110_WT_NC mouse_148_WT_C mouse_148_WT_NC
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 9.066601 7.044026 9.419500
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 4.153098 8.373006 3.632551
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 8.820855 11.258774 8.960279
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 8.975093 5.198449 9.079718
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 9.020096 7.062972 9.119441
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9.548425 7.355047 9.779434
mouse_158_WT_C mouse_158_WT_NC mouse_183_KOMIR150_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 6.774864 9.189456 6.793887
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 8.118558 3.391535 8.717340
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 11.074742 8.725945 11.030298
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 5.463973 9.204733 5.224246
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 7.396916 9.263360 7.186377
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 7.039108 9.734513 7.409819
mouse_183_KOMIR150_NC mouse_198_KOMIR150_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 9.272997 6.504482
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 3.500537 8.651096
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 8.699953 10.721178
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 8.878484 4.814123
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 8.798820 7.044256
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9.546336 6.547832
mouse_198_KOMIR150_NC mouse_206_KOMIR150_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 8.970438 6.444737
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 3.759714 8.756254
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 8.509122 10.797859
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 9.188250 5.239532
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 8.789968 6.946957
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9.308492 6.593036
mouse_206_KOMIR150_NC mouse_2670_KOTet3_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 8.900220 6.591024
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 3.625307 7.820674
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 8.504871 11.453482
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 9.469505 4.940524
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 8.835332 7.730090
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9.147440 7.796325
mouse_2670_KOTet3_NC mouse_7530_KOTet3_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 9.506520 6.425574
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 4.119562 8.236079
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 7.521391 11.185447
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 9.878697 4.042055
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 9.473214 7.437762
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 10.621108 7.347984
mouse_7530_KOTet3_NC mouse_7531_KOTet3_C mouse_7532_WT_NC
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 9.338409 6.259331 8.832075
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 3.283661 9.008766 4.523736
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 7.209527 11.317033 9.572427
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 9.446796 4.072264 8.995432
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 9.413081 7.322632 8.935514
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 10.445986 6.906662 9.512530
mouse_H510_WT_C mouse_H510_WT_NC mouse_H514_WT_C
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 6.444073 8.973037 6.480320
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 8.938437 4.565744 8.737141
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 11.428494 9.500517 11.193734
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 4.148818 8.994464 4.820109
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 6.811383 8.649953 7.141218
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 6.517112 9.429355 6.795476
mouse_H514_WT_NC
ENSMUSG00000020608.8 9.157573
ENSMUSG00000052212.7 4.328847
ENSMUSG00000049103.15 9.005364
ENSMUSG00000030203.18 9.165206
ENSMUSG00000027508.16 9.004301
ENSMUSG00000021990.17 9.585689
write.table ( top.table , file = "WT.C_v_WT.NC.txt" , row.names = F , sep = "\t" , quote = F )
Quiz 3
Submit Quiz
Linear models and contrasts
Let’s say we want to compare genotypes for cell type C. The only thing we have to change is the call to makeContrasts:
contr <- makeContrasts ( groupWT.C - groupKOMIR150.C , levels = colnames ( coef ( fit )))
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , contr )
tmp <- eBayes ( tmp )
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
head ( top.table , 20 )
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 -2.9794841 4.8093053 -15.526938 1.984025e-11 2.267740e-07
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 -3.2492483 6.8291795 -11.427311 2.283435e-09 1.304983e-05
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 -2.0785859 4.9242350 -9.047548 6.949803e-08 2.004156e-04
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 1.7327619 7.0657178 9.041700 7.013669e-08 2.004156e-04
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 -2.2538218 6.4431525 -8.746312 1.119185e-07 2.159461e-04
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 -5.2390560 5.0042592 -8.738328 1.133575e-07 2.159461e-04
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 -1.1948544 6.3048017 -7.961361 4.081414e-07 6.664367e-04
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 5.0046008 3.1239296 7.875918 4.720879e-07 6.744956e-04
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 0.8590031 7.2918397 7.238286 1.441887e-06 1.819292e-03
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 -1.2306749 7.5341308 -7.183294 1.591682e-06 1.819292e-03
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 1.0089083 6.6854527 7.038173 2.070079e-06 2.126368e-03
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 -5.6654297 2.3853315 -6.996774 2.232407e-06 2.126368e-03
ENSMUSG00000055435.7 -1.3884855 4.9736669 -6.793182 3.246993e-06 2.854856e-03
ENSMUSG00000028037.14 5.6397694 2.3452940 6.665050 4.122324e-06 3.365583e-03
ENSMUSG00000039146.6 7.4363964 0.1197785 6.577750 4.856537e-06 3.700681e-03
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 3.0830501 4.6808527 6.445119 6.242206e-06 4.254655e-03
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 -1.2964673 6.3304194 -6.437941 6.328008e-06 4.254655e-03
ENSMUSG00000051495.9 -0.8713110 7.1409081 -6.396919 6.842452e-06 4.344957e-03
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 -0.7267966 7.4673400 -6.359198 7.353816e-06 4.423901e-03
ENSMUSG00000096768.9 -1.9846810 3.4256738 -6.041035 1.360967e-05 7.777924e-03
B
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 16.0048436
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 11.8174038
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 8.3780060
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 8.4730364
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 7.8784993
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 7.0489500
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 6.6435962
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 4.8009371
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 5.2813342
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 5.1329930
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 5.0723354
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 2.2566477
ENSMUSG00000055435.7 4.6743751
ENSMUSG00000028037.14 3.0240161
ENSMUSG00000039146.6 0.9916291
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 3.6793908
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 3.8941452
ENSMUSG00000051495.9 3.6972150
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 3.5825789
ENSMUSG00000096768.9 3.3465594
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 )) # number of DE genes
[1] 44
top.table $ Gene <- rownames ( top.table )
top.table <- top.table [, c ( "Gene" , names ( top.table )[ 1 : 6 ])]
top.table <- data.frame ( top.table , anno [ match ( top.table $ Gene , anno $ Gene.stable.ID ),], logcpm [ match ( top.table $ Gene , rownames ( logcpm )),])
write.table ( top.table , file = "WT.C_v_KOMIR150.C.txt" , row.names = F , sep = "\t" , quote = F )
What if we refit our model as a two-factor model (rather than using the group variable)?
Create new model matrix:
genotype <- factor ( metadata $ genotype , levels = c ( "WT" , "KOMIR150" , "KOTet3" ))
cell_type <- factor ( metadata $ cell_type , levels = c ( "C" , "NC" ))
mouse <- factor ( metadata $ mouse , levels = c ( "110" , "148" , "158" , "183" , "198" , "206" , "2670" , "7530" , "7531" , "7532" , "H510" , "H514" ))
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ genotype * cell_type + mouse )
We are specifying that model includes effects for genotype, cell type, and the genotype-cell type interaction (which allows the differences between genotypes to differ across cell types).
[1] "(Intercept)" "genotypeKOMIR150"
[3] "genotypeKOTet3" "cell_typeNC"
[5] "mouse148" "mouse158"
[7] "mouse183" "mouse198"
[9] "mouse206" "mouse2670"
[11] "mouse7530" "mouse7531"
[13] "mouse7532" "mouseH510"
[15] "mouseH514" "genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC"
[17] "genotypeKOTet3:cell_typeNC"
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = F )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
(Intercept) genotypeKOMIR150 genotypeKOTet3 cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 4.759326 0.10393680 0.25235008 -0.135156622
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 5.519602 -0.38371523 0.11722570 -0.162972407
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 5.773644 0.11396426 -0.12628542 0.007554495
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 5.420424 -0.16072757 -0.03714907 -0.270138316
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 6.541454 -0.01828919 0.11896053 -0.251654329
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 1.883502 0.39754622 1.59130601 0.204158805
mouse148 mouse158 mouse183 mouse198 mouse206
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 0.23192176 0.16747528 -0.4528993 -0.10127318 NA
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 -0.03872025 0.04806943 0.3685759 0.41175400 NA
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.05756464 0.04179097 -0.2529610 -0.00841256 NA
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.16351899 -0.22593717 -0.3302039 0.06166284 NA
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 -0.10198768 -0.02426407 -0.1209212 0.12443747 NA
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 -0.10839188 0.11945290 -0.3786011 0.15564447 NA
mouse2670 mouse7530 mouse7531 mouse7532
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 -0.04037166 -0.009073243 NA 0.19499278
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.06371351 -0.116244875 NA 0.25787054
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.17471195 0.200158401 NA 0.06104751
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 0.13088790 0.391433836 NA -0.29436437
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 -0.09360513 -0.137224529 NA 0.18101608
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 -1.09960890 -0.199717680 NA 1.89832058
mouseH510 mouseH514 genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 0.16951088 0.15722271 0.38121760
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.10923179 0.22799700 0.28726735
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.04599131 -0.03185153 0.04419891
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.03879120 -0.15132577 0.09026355
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 0.01135225 -0.12996434 0.06953420
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 1.25166060 1.45045597 -0.05836709
genotypeKOTet3:cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 -0.1374981
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.1279962
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.1578704
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.2538109
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 0.3435573
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 0.1297337
[1] "(Intercept)" "genotypeKOMIR150"
[3] "genotypeKOTet3" "cell_typeNC"
[5] "mouse148" "mouse158"
[7] "mouse183" "mouse198"
[9] "mouse206" "mouse2670"
[11] "mouse7530" "mouse7531"
[13] "mouse7532" "mouseH510"
[15] "mouseH514" "genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC"
[17] "genotypeKOTet3:cell_typeNC"
The coefficient genotypeKOMIR150 represents the difference in mean expression between KOMIR150 and the reference genotype (WT), for cell type C (the reference level for cell type)
The coefficient cell_typeNC represents the difference in mean expression between cell type NC and cell type C, for genotype WT
The coefficient genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC is the difference between cell types NC and C of the differences between genotypes KOMIR150 and WT (the interaction effect).
Let’s estimate the difference between genotypes WT and KOMIR150 in cell type C.
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , coef = 2 ) # Directly test second coefficient
tmp <- eBayes ( tmp )
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
head ( top.table , 20 )
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 2.9794841 4.8093053 15.526938 1.984025e-11 2.267740e-07
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 3.2492483 6.8291795 11.427311 2.283435e-09 1.304983e-05
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 2.0785859 4.9242350 9.047548 6.949803e-08 2.004156e-04
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 -1.7327619 7.0657178 -9.041700 7.013669e-08 2.004156e-04
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 2.2538218 6.4431525 8.746312 1.119185e-07 2.159461e-04
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 5.2390560 5.0042592 8.738328 1.133575e-07 2.159461e-04
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 1.1948544 6.3048017 7.961361 4.081414e-07 6.664367e-04
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 -5.0046008 3.1239296 -7.875918 4.720879e-07 6.744956e-04
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 -0.8590031 7.2918397 -7.238286 1.441887e-06 1.819292e-03
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 1.2306749 7.5341308 7.183294 1.591682e-06 1.819292e-03
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 -1.0089083 6.6854527 -7.038173 2.070079e-06 2.126368e-03
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 5.6654297 2.3853315 6.996774 2.232407e-06 2.126368e-03
ENSMUSG00000055435.7 1.3884855 4.9736669 6.793182 3.246993e-06 2.854856e-03
ENSMUSG00000028037.14 -5.6397694 2.3452940 -6.665050 4.122324e-06 3.365583e-03
ENSMUSG00000039146.6 -7.4363964 0.1197785 -6.577750 4.856537e-06 3.700681e-03
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 -3.0830501 4.6808527 -6.445119 6.242206e-06 4.254655e-03
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 1.2964673 6.3304194 6.437941 6.328008e-06 4.254655e-03
ENSMUSG00000051495.9 0.8713110 7.1409081 6.396919 6.842452e-06 4.344957e-03
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 0.7267966 7.4673400 6.359198 7.353816e-06 4.423901e-03
ENSMUSG00000096768.9 1.9846810 3.4256738 6.041035 1.360967e-05 7.777924e-03
B
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 16.0048436
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 11.8174038
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 8.3780060
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 8.4730364
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 7.8784993
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 7.0489500
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 6.6435962
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 4.8009371
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 5.2813342
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 5.1329930
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 5.0723354
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 2.2566477
ENSMUSG00000055435.7 4.6743751
ENSMUSG00000028037.14 3.0240161
ENSMUSG00000039146.6 0.9916291
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 3.6793908
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 3.8941452
ENSMUSG00000051495.9 3.6972150
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 3.5825789
ENSMUSG00000096768.9 3.3465594
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 )) # number of DE genes
[1] 44
We get the same results as with the model where each coefficient corresponded to a group mean. In essence, these are the same model, so use whichever is most convenient for what you are estimating.
The interaction effects genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC are easier to estimate and test in this setup.
(Intercept) genotypeKOMIR150 genotypeKOTet3 cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 4.759326 0.10393680 0.25235008 -0.135156622
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 5.519602 -0.38371523 0.11722570 -0.162972407
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 5.773644 0.11396426 -0.12628542 0.007554495
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 5.420424 -0.16072757 -0.03714907 -0.270138316
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 6.541454 -0.01828919 0.11896053 -0.251654329
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 1.883502 0.39754622 1.59130601 0.204158805
mouse148 mouse158 mouse183 mouse198 mouse206
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 0.23192176 0.16747528 -0.4528993 -0.10127318 NA
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 -0.03872025 0.04806943 0.3685759 0.41175400 NA
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.05756464 0.04179097 -0.2529610 -0.00841256 NA
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.16351899 -0.22593717 -0.3302039 0.06166284 NA
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 -0.10198768 -0.02426407 -0.1209212 0.12443747 NA
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 -0.10839188 0.11945290 -0.3786011 0.15564447 NA
mouse2670 mouse7530 mouse7531 mouse7532
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 -0.04037166 -0.009073243 NA 0.19499278
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.06371351 -0.116244875 NA 0.25787054
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.17471195 0.200158401 NA 0.06104751
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 0.13088790 0.391433836 NA -0.29436437
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 -0.09360513 -0.137224529 NA 0.18101608
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 -1.09960890 -0.199717680 NA 1.89832058
mouseH510 mouseH514 genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 0.16951088 0.15722271 0.38121760
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.10923179 0.22799700 0.28726735
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.04599131 -0.03185153 0.04419891
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.03879120 -0.15132577 0.09026355
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 0.01135225 -0.12996434 0.06953420
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 1.25166060 1.45045597 -0.05836709
genotypeKOTet3:cell_typeNC
ENSMUSG00000033845.14 -0.1374981
ENSMUSG00000025903.15 0.1279962
ENSMUSG00000033813.16 0.1578704
ENSMUSG00000033793.13 -0.2538109
ENSMUSG00000025907.15 0.3435573
ENSMUSG00000090031.3 0.1297337
[1] "(Intercept)" "genotypeKOMIR150"
[3] "genotypeKOTet3" "cell_typeNC"
[5] "mouse148" "mouse158"
[7] "mouse183" "mouse198"
[9] "mouse206" "mouse2670"
[11] "mouse7530" "mouse7531"
[13] "mouse7532" "mouseH510"
[15] "mouseH514" "genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC"
[17] "genotypeKOTet3:cell_typeNC"
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , coef = 16 ) # Test genotypeKOMIR150:cell_typeNC
tmp <- eBayes ( tmp )
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
head ( top.table , 20 )
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000076609.3 -4.5128827 3.4659311 -4.633480 0.0002414512 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 0.7183028 7.0657178 4.604149 0.0002569486 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000033004.17 -0.3892516 8.7779980 -4.516015 0.0003098966 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000029004.16 -0.3441454 8.5115425 -4.317942 0.0004731874 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000054387.14 -0.3560405 7.9946594 -4.161984 0.0006615271 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000015501.11 -0.8394246 5.4932385 -4.125877 0.0007150204 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000004952.14 -0.4531030 7.8924221 -4.124182 0.0007176359 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000004110.18 -3.5672998 0.6672797 -4.064644 0.0008159243 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000030724.8 -2.8628699 1.0344703 -4.038959 0.0008624179 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000049313.9 0.3111176 9.7727059 4.023953 0.0008908099 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000026357.4 0.9360904 4.3871616 3.987096 0.0009646068 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000070305.11 1.6482356 3.4354823 3.983690 0.0009717289 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000032026.8 -0.6465648 5.6058186 -3.962272 0.0010177514 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000029647.16 -0.3420436 7.5824112 -3.916955 0.0011224903 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000037020.17 -0.9135733 3.9978898 -3.831876 0.0013492919 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000110218.2 -1.8853554 2.5480596 -3.831485 0.0013504314 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 -0.6784186 6.3304194 -3.810327 0.0014137014 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000005533.11 -0.8335725 5.6296782 -3.779567 0.0015110233 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000037857.17 -0.3611968 7.5179818 -3.758815 0.0015804456 0.7596173
ENSMUSG00000071757.11 -0.7414184 4.6233742 -3.752057 0.0016037349 0.7596173
B
ENSMUSG00000076609.3 -0.588024711
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 0.600834785
ENSMUSG00000033004.17 0.399962669
ENSMUSG00000029004.16 0.002697595
ENSMUSG00000054387.14 -0.287399318
ENSMUSG00000015501.11 -0.356637749
ENSMUSG00000004952.14 -0.350694576
ENSMUSG00000004110.18 -2.817938460
ENSMUSG00000030724.8 -2.497016729
ENSMUSG00000049313.9 -0.676513504
ENSMUSG00000026357.4 -0.848600918
ENSMUSG00000070305.11 -1.666705769
ENSMUSG00000032026.8 -0.633243118
ENSMUSG00000029647.16 -0.762087269
ENSMUSG00000037020.17 -1.293822376
ENSMUSG00000110218.2 -2.213357837
ENSMUSG00000024772.10 -0.913573355
ENSMUSG00000005533.11 -0.960473010
ENSMUSG00000037857.17 -1.082554261
ENSMUSG00000071757.11 -1.189111084
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 ))
[1] 0
The log fold change here is the difference between genotypes KOMIR150 and WT in the log fold changes between cell types NC and C.
A gene for which this interaction effect is significant is one for which the effect of cell type differs between genotypes, and for which the effect of genotypes differs between cell types.
More complicated models
Specifying a different model is simply a matter of changing the calls to model.matrix (and possibly to contrasts.fit).
What if we want to adjust for a continuous variable like some health score?
(We are making this data up here, but it would typically be a variable in your metadata.)
# Generate example health data
set.seed ( 99 )
HScore <- rnorm ( n = 22 , mean = 7.5 , sd = 1 )
HScore
[1] 7.713963 7.979658 7.587829 7.943859 7.137162 7.622674 6.636155 7.989624
[9] 7.135883 6.205758 6.754231 8.421550 8.250054 4.991446 4.459066 7.500266
[17] 7.105981 5.754972 7.998631 7.770954 8.598922 8.252513
Model adjusting for HScore score:
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ 0 + group + mouse + HScore )
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = F )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
contr <- makeContrasts ( groupKOMIR150.NC - groupWT.NC ,
levels = colnames ( coef ( fit )))
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , contr )
tmp <- eBayes ( tmp )
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
head ( top.table , 20 )
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 3.1986356 6.829179 20.798209 1.962669e-13 2.243331e-09
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 3.2473693 4.809305 14.828550 4.370936e-11 2.185013e-07
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 5.5005605 5.004259 14.573680 5.734941e-11 2.185013e-07
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 5.6322648 2.385331 10.479904 8.659567e-09 2.474471e-05
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 3.0346995 6.443152 10.021618 1.664686e-08 3.805472e-05
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 1.3194480 6.304802 9.481425 3.700926e-08 7.050264e-05
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 -2.8305758 4.680853 -9.068882 6.963269e-08 1.137002e-04
ENSMUSG00000070372.12 0.9128162 7.401010 8.566272 1.545088e-07 1.943775e-04
ENSMUSG00000100801.2 -2.5198136 5.600966 -8.480951 1.774318e-07 1.943775e-04
ENSMUSG00000042396.11 -1.0158466 6.739812 -8.457085 1.844617e-07 1.943775e-04
ENSMUSG00000028173.11 -1.7945862 6.802367 -8.432737 1.919347e-07 1.943775e-04
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 1.1014376 7.534131 8.395236 2.040708e-07 1.943775e-04
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 -1.0464662 6.685453 -8.147177 3.074957e-07 2.703597e-04
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 -1.0076392 7.065718 -7.823229 5.314964e-07 4.339288e-04
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 1.8451380 4.924235 7.486638 9.522044e-07 7.255798e-04
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 -3.9015255 3.123930 -7.383692 1.141519e-06 8.097675e-04
ENSMUSG00000035212.15 0.8127757 7.115543 7.353414 1.204379e-06 8.097675e-04
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 -0.8008633 7.291840 -6.909792 2.679195e-06 1.701289e-03
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 0.6818400 7.467340 6.680298 4.094477e-06 2.463151e-03
ENSMUSG00000063065.14 -0.6195530 7.926770 -6.629172 4.504617e-06 2.574388e-03
B
ENSMUSG00000044229.10 20.631543
ENSMUSG00000030703.9 14.663658
ENSMUSG00000032012.10 13.740069
ENSMUSG00000096780.8 6.451388
ENSMUSG00000040152.9 9.846582
ENSMUSG00000008348.10 9.079941
ENSMUSG00000028619.16 7.794944
ENSMUSG00000070372.12 7.564819
ENSMUSG00000100801.2 7.520317
ENSMUSG00000042396.11 7.471668
ENSMUSG00000028173.11 7.455922
ENSMUSG00000020893.18 7.285023
ENSMUSG00000030365.12 7.010470
ENSMUSG00000030748.10 6.388897
ENSMUSG00000066687.6 5.830311
ENSMUSG00000067017.6 3.895938
ENSMUSG00000035212.15 5.544300
ENSMUSG00000028028.12 4.741840
ENSMUSG00000042105.19 4.276939
ENSMUSG00000063065.14 4.115024
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 ))
[1] 103
What if we want to look at the correlation of gene expression with a continuous variable like pH?
# Generate example pH data
set.seed ( 99 )
pH <- rnorm ( n = 22 , mean = 8 , sd = 1.5 )
pH
[1] 8.320944 8.719487 8.131743 8.665788 7.455743 8.184011 6.704232 8.734436
[9] 7.453825 6.058637 6.881346 9.382326 9.125082 4.237169 3.438599 8.000399
[17] 7.408972 5.382459 8.747947 8.406431 9.648382 9.128770
Specify model matrix:
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ pH )
head ( mm )
(Intercept) pH
1 1 8.320944
2 1 8.719487
3 1 8.131743
4 1 8.665788
5 1 7.455743
6 1 8.184011
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = F )
fit <- lmFit ( y , mm )
tmp <- contrasts.fit ( fit , coef = 2 ) # test "pH" coefficient
tmp <- eBayes ( tmp )
top.table <- topTable ( tmp , sort.by = "P" , n = Inf )
head ( top.table , 20 )
logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val
ENSMUSG00000056054.10 -1.19254531 1.0565449 -5.157240 3.209341e-05 0.3446698
ENSMUSG00000094497.2 -0.96444255 -0.6307376 -4.743286 8.937725e-05 0.3446698
ENSMUSG00000026822.15 -1.16854887 1.2606660 -4.738417 9.046451e-05 0.3446698
ENSMUSG00000027111.17 -0.51910960 2.3918569 -4.192738 3.514725e-04 0.8962289
ENSMUSG00000069049.12 -1.20135365 1.5709261 -4.148768 3.920511e-04 0.8962289
ENSMUSG00000056071.13 -1.00722461 0.8964826 -3.869205 7.837864e-04 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000069045.12 -1.22876298 2.0766487 -3.817404 8.906755e-04 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000036764.13 -0.32538482 0.2918326 -3.639265 1.380051e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000016356.19 0.26379202 1.6897369 3.583084 1.583377e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000046032.17 -0.07888075 5.1634625 -3.570693 1.632028e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000056673.15 -1.11017031 1.1242042 -3.558301 1.682153e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000091537.3 -0.09566601 5.4139203 -3.549457 1.718843e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000068457.15 -0.88173101 0.1963880 -3.494321 1.965895e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000040521.12 -0.17464621 2.8725902 -3.479532 2.037862e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000027132.4 -0.15648374 3.3593172 -3.464016 2.116141e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000035877.18 -0.16427058 2.7431464 -3.463779 2.117359e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000015312.10 -0.13194795 3.2827835 -3.457202 2.151436e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000090946.4 -0.10217641 5.8052578 -3.426513 2.317658e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000037316.10 -0.10364133 4.1993268 -3.425346 2.324218e-03 0.9995090
ENSMUSG00000062981.6 -0.11263761 4.7741304 -3.362498 2.705680e-03 0.9995090
B
ENSMUSG00000056054.10 0.1923229
ENSMUSG00000094497.2 -1.8395832
ENSMUSG00000026822.15 -0.2473300
ENSMUSG00000027111.17 -0.4559397
ENSMUSG00000069049.12 -0.6876277
ENSMUSG00000056071.13 -1.7276316
ENSMUSG00000069045.12 -1.0462003
ENSMUSG00000036764.13 -2.7849384
ENSMUSG00000016356.19 -2.6851059
ENSMUSG00000046032.17 -1.0977551
ENSMUSG00000056673.15 -1.8998096
ENSMUSG00000091537.3 -1.1363154
ENSMUSG00000068457.15 -2.5177382
ENSMUSG00000040521.12 -1.6427259
ENSMUSG00000027132.4 -1.5204128
ENSMUSG00000035877.18 -1.7121170
ENSMUSG00000015312.10 -1.5534278
ENSMUSG00000090946.4 -1.3938223
ENSMUSG00000037316.10 -1.4481510
ENSMUSG00000062981.6 -1.5303786
length ( which ( top.table $ adj.P.Val < 0.05 ))
[1] 0
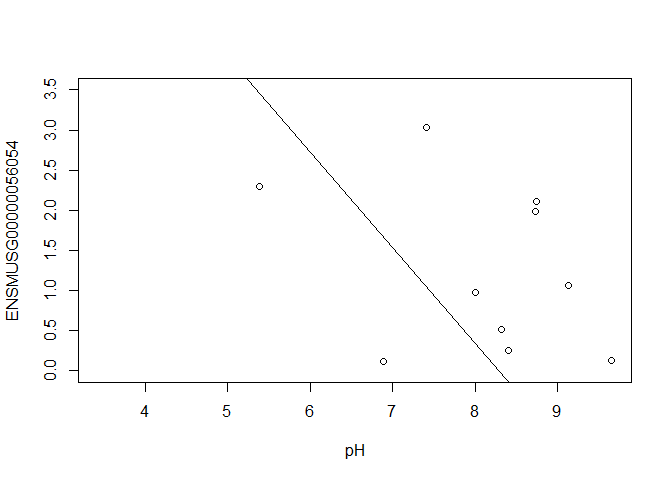
In this case, limma is fitting a linear regression model, which here is a straight line fit, with the slope and intercept defined by the model coefficients:
ENSMUSG00000056054 <- y $ E [ "ENSMUSG00000056054.10" ,]
plot ( ENSMUSG00000056054 ~ pH , ylim = c ( 0 , 3.5 ))
intercept <- coef ( fit )[ "ENSMUSG00000056054.10" , "(Intercept)" ]
slope <- coef ( fit )[ "ENSMUSG00000056054.10" , "pH" ]
abline ( a = intercept , b = slope )
[1] -1.192545
In this example, the log fold change logFC is the slope of the line, or the change in gene expression (on the log2 CPM scale) for each unit increase in pH.
Here, a logFC of 0.20 means a 0.20 log2 CPM increase in gene expression for each unit increase in pH, or a 15% increase on the CPM scale (2^0.20 = 1.15).
A bit more on linear models
Limma fits a linear model to each gene.
Linear models include analysis of variance (ANOVA) models, linear regression, and any model of the form
Y = β0 + β1 X1 + β2 X2 + … + βp Xp + ε
The covariates X can be:
a continuous variable (pH, HScore score, age, weight, temperature, etc.)
Dummy variables coding a categorical covariate (like cell type, genotype, and group)
The β’s are unknown parameters to be estimated.
In limma, the β’s are the log fold changes.
The error (residual) term ε is assumed to be normally distributed with a variance that is constant across the range of the data.
Normally distributed means the residuals come from a distribution that looks like this:
The log2 transformation that voom applies to the counts makes the data “normal enough”, but doesn’t completely stabilize the variance:
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ 0 + group + mouse )
tmp <- voom ( d , mm , plot = T )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
The log2 counts per million are more variable at lower expression levels. The variance weights calculated by voom address this situation.
Both edgeR and limma have VERY comprehensive user manuals
The limma users’ guide has great details on model specification.
Quiz 4
Submit Quiz
Simple plotting
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ genotype * cell_type + mouse )
colnames ( mm ) <- make.names ( colnames ( mm ))
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = F )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
contrast.matrix <- makeContrasts ( genotypeKOMIR150 , levels = colnames ( coef ( fit )))
fit2 <- contrasts.fit ( fit , contrast.matrix )
fit2 <- eBayes ( fit2 )
top.table <- topTable ( fit2 , coef = 1 , sort.by = "P" , n = 40 )
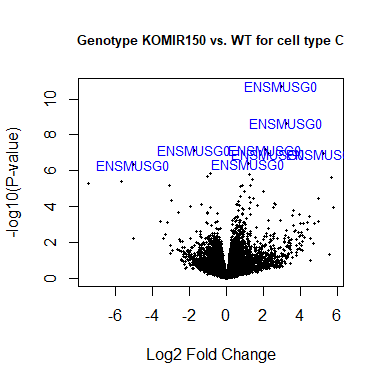
Volcano plot
volcanoplot ( fit2 , coef = 1 , highlight = 8 , names = rownames ( fit2 ), main = "Genotype KOMIR150 vs. WT for cell type C" , cex.main = 0.8 )
head ( anno [ match ( rownames ( fit2 ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ),
c ( "Gene.stable.ID.version" , "Gene.name" ) ])
Gene.stable.ID.version Gene.name
48204 ENSMUSG00000033845.14 Mrpl15
48494 ENSMUSG00000025903.15 Lypla1
48624 ENSMUSG00000033813.16 Tcea1
49101 ENSMUSG00000033793.13 Atp6v1h
49316 ENSMUSG00000025907.15 Rb1cc1
49363 ENSMUSG00000090031.3 4732440D04Rik
identical ( anno [ match ( rownames ( fit2 ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ),
c ( "Gene.stable.ID.version" )], rownames ( fit2 ))
[1] TRUE
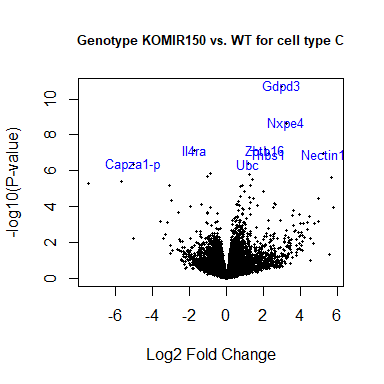
volcanoplot ( fit2 , coef = 1 , highlight = 8 , names = anno [ match ( rownames ( fit2 ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ), "Gene.name" ], main = "Genotype KOMIR150 vs. WT for cell type C" , cex.main = 0.8 )
Heatmap
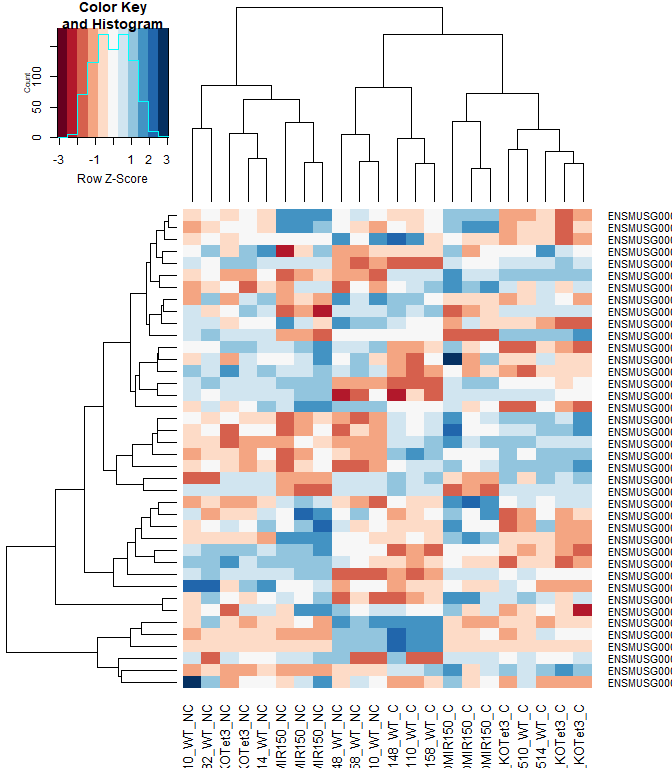
#using a red and blue color scheme without traces and scaling each row
heatmap.2 ( logcpm [ rownames ( top.table ),], col = brewer.pal ( 11 , "RdBu" ), scale = "row" , trace = "none" )
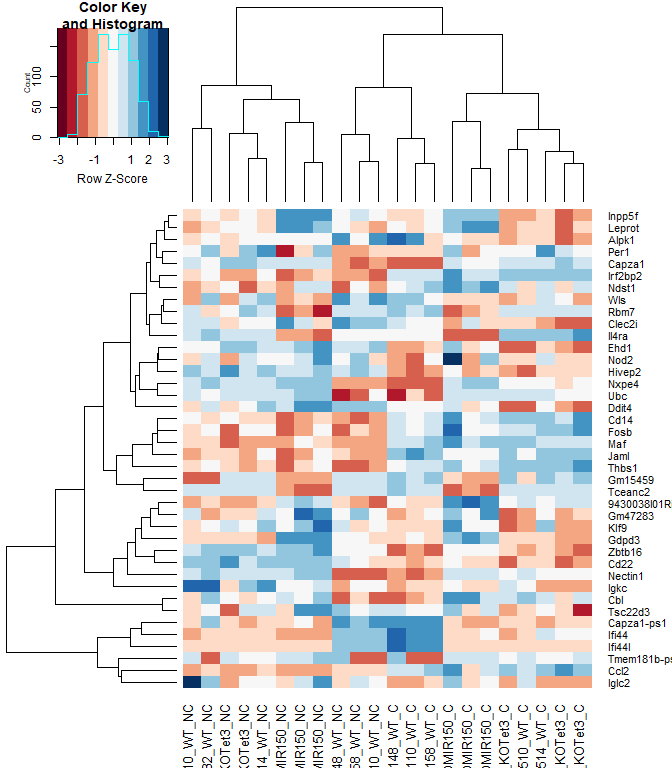
anno [ match ( rownames ( top.table ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ),
c ( "Gene.stable.ID.version" , "Gene.name" )]
Gene.stable.ID.version Gene.name
14757 ENSMUSG00000030703.9 Gdpd3
42161 ENSMUSG00000044229.10 Nxpe4
4197 ENSMUSG00000066687.6 Zbtb16
53114 ENSMUSG00000030748.10 Il4ra
54774 ENSMUSG00000040152.9 Thbs1
25330 ENSMUSG00000032012.10 Nectin1
38111 ENSMUSG00000008348.10 Ubc
47471 ENSMUSG00000067017.6 Capza1-ps1
21965 ENSMUSG00000028028.12 Alpk1
43237 ENSMUSG00000020893.18 Per1
27431 ENSMUSG00000030365.12 Clec2i
25483 ENSMUSG00000096780.8 Tmem181b-ps
20046 ENSMUSG00000055435.7 Maf
3037 ENSMUSG00000028037.14 Ifi44
3066 ENSMUSG00000039146.6 Ifi44l
8128 ENSMUSG00000028619.16 Tceanc2
11049 ENSMUSG00000024772.10 Ehd1
33286 ENSMUSG00000051495.9 Irf2bp2
40360 ENSMUSG00000042105.19 Inpp5f
845 ENSMUSG00000096768.9 Gm47283
2174 ENSMUSG00000054008.10 Ndst1
38893 ENSMUSG00000070372.12 Capza1
24249 ENSMUSG00000055994.16 Nod2
17223 ENSMUSG00000076937.4 Iglc2
1787 ENSMUSG00000033863.3 Klf9
11765 ENSMUSG00000100801.2 Gm15459
42225 ENSMUSG00000035212.15 Leprot
9792 ENSMUSG00000051439.8 Cd14
42439 ENSMUSG00000035385.6 Ccl2
28025 ENSMUSG00000034342.10 Cbl
20508 ENSMUSG00000028173.11 Wls
28896 ENSMUSG00000003545.4 Fosb
23841 ENSMUSG00000031431.14 Tsc22d3
51382 ENSMUSG00000040139.15 9430038I01Rik
26357 ENSMUSG00000020108.5 Ddit4
37483 ENSMUSG00000048534.8 Jaml
7652 ENSMUSG00000076609.3 Igkc
50026 ENSMUSG00000030577.15 Cd22
4064 ENSMUSG00000042396.11 Rbm7
36006 ENSMUSG00000015501.11 Hivep2
identical ( anno [ match ( rownames ( top.table ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ), "Gene.stable.ID.version" ], rownames ( top.table ))
[1] TRUE
heatmap.2 ( logcpm [ rownames ( top.table ),], col = brewer.pal ( 11 , "RdBu" ), scale = "row" , trace = "none" , labRow = anno [ match ( rownames ( top.table ), anno $ Gene.stable.ID.version ), "Gene.name" ])
2 factor venn diagram
mm <- model.matrix ( ~ genotype * cell_type + mouse )
colnames ( mm ) <- make.names ( colnames ( mm ))
y <- voom ( d , mm , plot = F )
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
Coefficients not estimable: mouse206 mouse7531
Warning: Partial NA coefficients for 11430 probe(s)
contrast.matrix <- makeContrasts ( genotypeKOMIR150 , genotypeKOMIR150 + genotypeKOMIR150.cell_typeNC , levels = colnames ( coef ( fit )))
fit2 <- contrasts.fit ( fit , contrast.matrix )
fit2 <- eBayes ( fit2 )
top.table <- topTable ( fit2 , coef = 1 , sort.by = "P" , n = 40 )
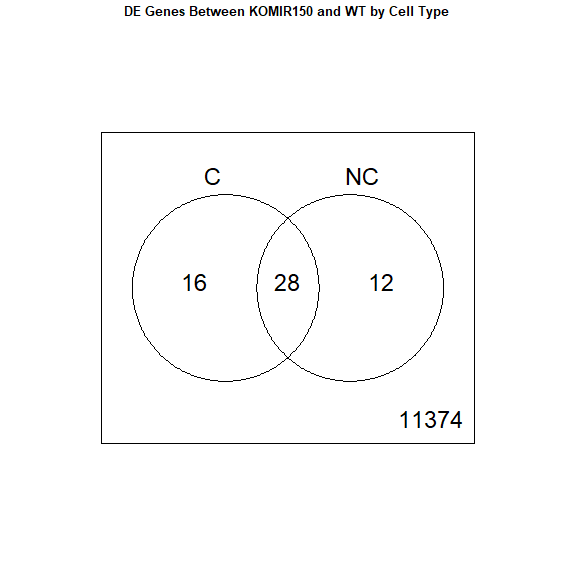
results <- decideTests ( fit2 )
vennDiagram ( results , names = c ( "C" , "NC" ), main = "DE Genes Between KOMIR150 and WT by Cell Type" , cex.main = 0.8 )
Download the Enrichment Analysis R Markdown document
download.file ( "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ucdavis-bioinformatics-training/2020-mRNA_Seq_Workshop/master/data_analysis/enrichment_mm.Rmd" , "enrichment_mm.Rmd" )
R version 4.2.0 (2022-04-22 ucrt)
Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit)
Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 19044)
Matrix products: default
locale:
[1] LC_COLLATE=English_United States.utf8
[2] LC_CTYPE=English_United States.utf8
[3] LC_MONETARY=English_United States.utf8
[4] LC_NUMERIC=C
[5] LC_TIME=English_United States.utf8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] gplots_3.1.3 RColorBrewer_1.1-3 edgeR_3.38.1 limma_3.52.1
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_1.0.8.3 knitr_1.39 magrittr_2.0.3 lattice_0.20-45
[5] R6_2.5.1 rlang_1.0.2 fastmap_1.1.0 highr_0.9
[9] stringr_1.4.0 caTools_1.18.2 tools_4.2.0 grid_4.2.0
[13] xfun_0.31 KernSmooth_2.23-20 cli_3.3.0 jquerylib_0.1.4
[17] htmltools_0.5.2 gtools_3.9.2.2 yaml_2.3.5 digest_0.6.29
[21] bitops_1.0-7 sass_0.4.1 evaluate_0.15 rmarkdown_2.14
[25] stringi_1.7.6 compiler_4.2.0 bslib_0.3.1 locfit_1.5-9.5
[29] jsonlite_1.8.0