Using the Phyloseq package
The phyloseq package is fast becoming a good way a managing micobial community data, filtering and visualizing that data and performing analysis such as ordination. Along with the standard R environment and packages vegan and vegetarian you can perform virtually any analysis. Today we will
- Load data straight from dbcAmplicons (biom file)
- Filter out Phylum
- Filter out additional Taxa
- Filter out samples
- Graphical Summaries
- Ordination
- Differential Abundances
Load our libraries
library(phyloseq)
library(biomformat)
library(ggplot2)
library(gridExtra)
library(vegan)
## Loading required package: permute
## Loading required package: lattice
## This is vegan 2.5-6
library(edgeR)
## Loading required package: limma
Read in the dataset, biom file generated from dbcAmplicons pipeline
First read in the dataset, see what the objects look like. Our Biom file, produces 3 tables: otu_table, taxa_table, sample_data. Look at the head of each. Get the sample names and tax ranks, finally view the phyloseq object. Lets draw a first bar plot.
s16sV3V5 = import_biom(BIOMfilename = "16sV3V5.biom", parseFunction = parse_taxonomy_default)
# this changes the columns names to kingdon through genus
colnames(tax_table(s16sV3V5)) <- c("Kingdom", "Phylum", "Class", "Order", "Family", "Genus")
head(otu_table(s16sV3V5))
## OTU Table: [6 taxa and 48 samples]
## taxa are rows
## sample1 sample10 sample11 sample12 sample13 sample14 sample15
## Taxa_00000 2144 2303 3235 2895 2584 2465 2907
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 29 18 40 36 33 42 37
## Taxa_00003 14 18 16 16 36 21 32
## Taxa_00004 142 138 214 136 88 132 148
## Taxa_00005 3 14 15 16 7 10 7
## sample16 sample17 sample18 sample19 sample2 sample20 sample21
## Taxa_00000 2651 2751 3022 2904 3034 2547 2908
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 35 42 25 40 19 43 34
## Taxa_00003 23 19 12 16 37 25 13
## Taxa_00004 140 141 131 109 140 227 227
## Taxa_00005 6 6 4 8 12 3 9
## sample22 sample23 sample24 sample25 sample26 sample27 sample28
## Taxa_00000 1946 2790 2146 2291 2046 2283 2292
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 24 32 33 23 23 21 26
## Taxa_00003 14 15 20 15 16 11 20
## Taxa_00004 90 161 105 135 104 93 99
## Taxa_00005 10 3 3 10 3 13 4
## sample29 sample3 sample30 sample31 sample32 sample33 sample34
## Taxa_00000 2349 2483 2126 2336 2576 2478 1909
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 34 22 27 33 33 26 28
## Taxa_00003 27 21 14 18 23 12 16
## Taxa_00004 137 163 188 107 200 99 176
## Taxa_00005 1 5 7 8 12 6 5
## sample35 sample36 sample37 sample38 sample39 sample4 sample40
## Taxa_00000 2666 2672 2605 2403 2552 2795 2073
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 36 28 19 34 28 39 28
## Taxa_00003 30 28 19 15 31 17 22
## Taxa_00004 319 202 271 203 170 133 89
## Taxa_00005 2 8 3 0 6 7 8
## sample41 sample42 sample43 sample44 sample45 sample46 sample47
## Taxa_00000 2519 3647 3352 3559 3270 2337 2835
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
## Taxa_00002 30 44 34 41 29 28 21
## Taxa_00003 14 39 21 28 31 17 28
## Taxa_00004 160 212 222 284 236 178 187
## Taxa_00005 2 10 8 4 5 10 8
## sample48 sample5 sample6 sample7 sample8 sample9
## Taxa_00000 2258 2214 3315 3078 2848 3107
## Taxa_00001 0 0 0 1 0 0
## Taxa_00002 29 28 27 35 32 35
## Taxa_00003 25 26 33 27 34 24
## Taxa_00004 146 195 185 399 310 241
## Taxa_00005 6 3 12 4 3 2
head(sample_data(s16sV3V5))
## primers Replicate Treatment Timepoint
## sample1 16S_V3V5 4 ABC_Control T1
## sample10 16S_V3V5 1 Control T2
## sample11 16S_V3V5 2 Control T2
## sample12 16S_V3V5 3 Control T2
## sample13 16S_V3V5 4 Control T2
## sample14 16S_V3V5 1 Condition1 T2
head(tax_table(s16sV3V5))
## Taxonomy Table: [6 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks]:
## Kingdom Phylum
## Taxa_00000 "d__Bacteria" NA
## Taxa_00001 "d__Bacteria" "p__Acetothermia"
## Taxa_00002 "d__Bacteria" "p__Acidobacteria"
## Taxa_00003 "d__Bacteria" "p__Acidobacteria"
## Taxa_00004 "d__Bacteria" "p__Acidobacteria"
## Taxa_00005 "d__Bacteria" "p__Acidobacteria"
## Class
## Taxa_00000 NA
## Taxa_00001 "c__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis"
## Taxa_00002 NA
## Taxa_00003 "c__Acidobacteria_Gp1"
## Taxa_00004 "c__Acidobacteria_Gp10"
## Taxa_00005 "c__Acidobacteria_Gp11"
## Order
## Taxa_00000 NA
## Taxa_00001 "o__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis"
## Taxa_00002 NA
## Taxa_00003 NA
## Taxa_00004 "o__Gp10"
## Taxa_00005 "o__Gp11"
## Family
## Taxa_00000 NA
## Taxa_00001 "f__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis"
## Taxa_00002 NA
## Taxa_00003 NA
## Taxa_00004 "f__Gp10"
## Taxa_00005 "f__Gp11"
## Genus
## Taxa_00000 NA
## Taxa_00001 "g__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis"
## Taxa_00002 NA
## Taxa_00003 NA
## Taxa_00004 "g__Gp10"
## Taxa_00005 "g__Gp11"
rank_names(s16sV3V5)
## [1] "Kingdom" "Phylum" "Class" "Order" "Family" "Genus"
sample_variables(s16sV3V5)
## [1] "primers" "Replicate" "Treatment" "Timepoint"
s16sV3V5
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 1344 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 1344 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
plot_bar(s16sV3V5, fill = "Phylum") + theme(legend.position="bottom" ) + scale_fill_manual(values = rainbow(length(unique(tax_table(s16sV3V5)[,"Phylum"]))-1))
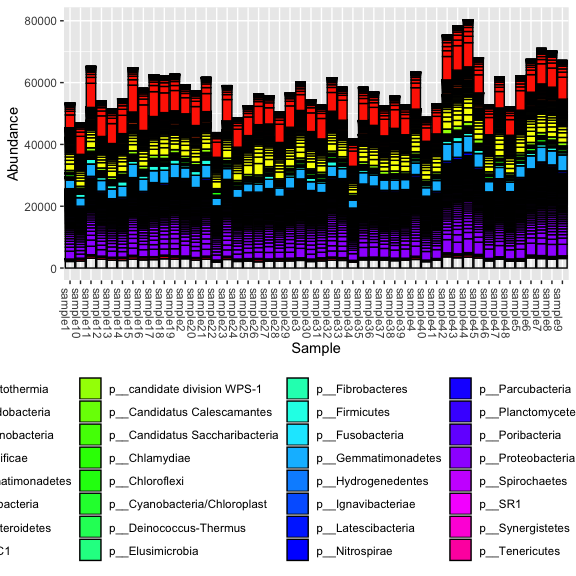
Filtering our dataset
First lets remove of the feature with ambiguous phylum annotation.
s16sV3V5 <- subset_taxa(s16sV3V5, !is.na(Phylum) & !Phylum %in% c("", "uncharacterized"))
s16sV3V5
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 1342 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 1342 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
Lets generate a prevelance table (number of samples each taxa occurs in) for each taxa.
prevelancedf = apply(X = otu_table(s16sV3V5),
MARGIN = 1,
FUN = function(x){sum(x > 0)})
# Add taxonomy and total read counts to this data.frame
prevelancedf = data.frame(Prevalence = prevelancedf,
TotalAbundance = taxa_sums(s16sV3V5),
tax_table(s16sV3V5))
colnames(prevelancedf) <- c("Prevalence", "TotalAbundance", colnames(tax_table(s16sV3V5)))
prevelancedf[1:10,]
## Prevalence TotalAbundance Kingdom Phylum
## Taxa_00001 1 1 d__Bacteria p__Acetothermia
## Taxa_00002 48 1483 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00003 48 1049 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00004 48 8312 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00005 47 321 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00006 23 34 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00007 8 13 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00008 48 1356 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00009 48 7213 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Taxa_00010 48 2285 d__Bacteria p__Acidobacteria
## Class
## Taxa_00001 c__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis
## Taxa_00002 <NA>
## Taxa_00003 c__Acidobacteria_Gp1
## Taxa_00004 c__Acidobacteria_Gp10
## Taxa_00005 c__Acidobacteria_Gp11
## Taxa_00006 c__Acidobacteria_Gp12
## Taxa_00007 c__Acidobacteria_Gp13
## Taxa_00008 c__Acidobacteria_Gp15
## Taxa_00009 c__Acidobacteria_Gp16
## Taxa_00010 c__Acidobacteria_Gp17
## Order
## Taxa_00001 o__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis
## Taxa_00002 <NA>
## Taxa_00003 <NA>
## Taxa_00004 o__Gp10
## Taxa_00005 o__Gp11
## Taxa_00006 o__Gp12
## Taxa_00007 o__Gp13
## Taxa_00008 o__Gp15
## Taxa_00009 o__Gp16
## Taxa_00010 o__Gp17
## Family
## Taxa_00001 f__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis
## Taxa_00002 <NA>
## Taxa_00003 <NA>
## Taxa_00004 f__Gp10
## Taxa_00005 f__Gp11
## Taxa_00006 f__Gp12
## Taxa_00007 f__Gp13
## Taxa_00008 f__Gp15
## Taxa_00009 f__Gp16
## Taxa_00010 f__Gp17
## Genus
## Taxa_00001 g__Acetothermia_genera_incertae_sedis
## Taxa_00002 <NA>
## Taxa_00003 <NA>
## Taxa_00004 g__Gp10
## Taxa_00005 g__Gp11
## Taxa_00006 g__Gp12
## Taxa_00007 g__Gp13
## Taxa_00008 g__Gp15
## Taxa_00009 g__Gp16
## Taxa_00010 g__Gp17
Whole phylum filtering
Now lets investigate low prevelance/abundance phylum and subset them out.
summary_prevalence <- plyr::ddply(prevelancedf, "Phylum", function(df1){
data.frame(mean_prevalence=mean(df1$Prevalence),total_abundance=sum(df1$TotalAbundance,na.rm = T),stringsAsFactors = F)
})
summary_prevalence
## Phylum mean_prevalence total_abundance
## 1 p__Acetothermia 1.00000 1
## 2 p__Acidobacteria 35.72973 521716
## 3 p__Actinobacteria 23.36910 171632
## 4 p__Aquificae 15.00000 72
## 5 p__Armatimonadetes 33.57143 2966
## 6 p__Atribacteria 8.00000 10
## 7 p__Bacteroidetes 24.49618 451903
## 8 p__BRC1 48.00000 451
## 9 p__candidate division WPS-1 48.00000 40707
## 10 p__Candidatus Calescamantes 1.00000 1
## 11 p__Candidatus Saccharibacteria 48.00000 14731
## 12 p__Chlamydiae 20.50000 514
## 13 p__Chloroflexi 33.51724 54899
## 14 p__Cyanobacteria/Chloroplast 23.84615 3738
## 15 p__Deinococcus-Thermus 3.75000 19
## 16 p__Elusimicrobia 25.33333 208
## 17 p__Fibrobacteres 25.00000 496
## 18 p__Firmicutes 13.02542 67371
## 19 p__Fusobacteria 1.00000 2
## 20 p__Gemmatimonadetes 48.00000 174765
## 21 p__Hydrogenedentes 33.00000 90
## 22 p__Ignavibacteriae 31.33333 447
## 23 p__Latescibacteria 48.00000 471
## 24 p__Nitrospirae 25.00000 25979
## 25 p__Parcubacteria 48.00000 477
## 26 p__Planctomycetes 37.86364 19036
## 27 p__Poribacteria 9.00000 13
## 28 p__Proteobacteria 25.16216 1090361
## 29 p__Spirochaetes 14.12500 424
## 30 p__SR1 14.00000 24
## 31 p__Synergistetes 3.25000 13
## 32 p__Tenericutes 7.50000 57
## 33 p__Thermodesulfobacteria 9.00000 14
## 34 p__Thermotogae 1.00000 2
## 35 p__Verrucomicrobia 33.40909 43057
Using the table above, determine the phyla to filter
sum(summary_prevalence$total_abundance)*0.001
## [1] 2686.667
table(summary_prevalence$total_abundance/sum(summary_prevalence$total_abundance) >= 0.001)
##
## FALSE TRUE
## 21 14
keepPhyla <- summary_prevalence$Phylum[summary_prevalence$total_abundance/sum(summary_prevalence$total_abundance) >= 0.001]
s16sV3V5.1 = subset_taxa(s16sV3V5, Phylum %in% keepPhyla)
summary_prevalence <- summary_prevalence[summary_prevalence$Phylum %in% keepPhyla,]
summary_prevalence
## Phylum mean_prevalence total_abundance
## 2 p__Acidobacteria 35.72973 521716
## 3 p__Actinobacteria 23.36910 171632
## 5 p__Armatimonadetes 33.57143 2966
## 7 p__Bacteroidetes 24.49618 451903
## 9 p__candidate division WPS-1 48.00000 40707
## 11 p__Candidatus Saccharibacteria 48.00000 14731
## 13 p__Chloroflexi 33.51724 54899
## 14 p__Cyanobacteria/Chloroplast 23.84615 3738
## 18 p__Firmicutes 13.02542 67371
## 20 p__Gemmatimonadetes 48.00000 174765
## 24 p__Nitrospirae 25.00000 25979
## 26 p__Planctomycetes 37.86364 19036
## 28 p__Proteobacteria 25.16216 1090361
## 35 p__Verrucomicrobia 33.40909 43057
s16sV3V5.1
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 1290 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 1290 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
Individual Taxa Filtering
Subset to the remaining phyla by prevelance.
prevelancedf1 = subset(prevelancedf, Phylum %in% get_taxa_unique(s16sV3V5.1, taxonomic.rank = "Phylum"))
ggplot(prevelancedf1, aes(TotalAbundance,Prevalence / nsamples(s16sV3V5.1),color=Phylum)) +
# Include a guess for parameter
geom_hline(yintercept = 0.10, alpha = 0.5, linetype = 2) + geom_point(size = 2, alpha = 0.7) +
scale_x_log10() + xlab("Total Abundance") + ylab("Prevalence [Frac. Samples]") +
facet_wrap(~Phylum) + theme(legend.position="none")
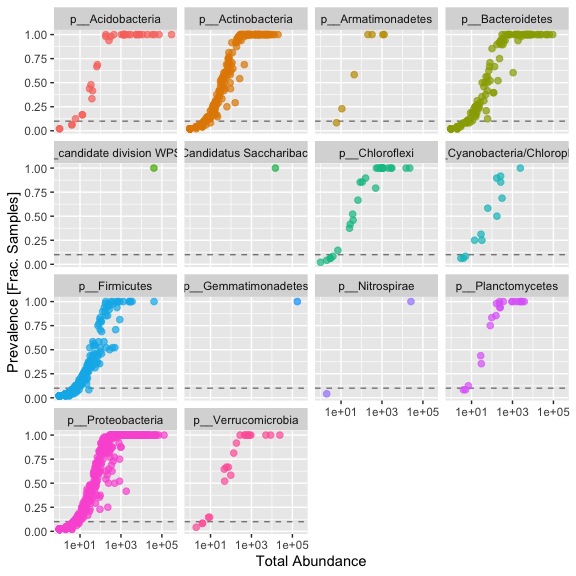
Sometimes you see a clear break, however we aren’t seeing one here. In this case I’m moslty interested in those organisms consistantly present in the dataset, so I’m removing all taxa present in less than 50% of samples.
# Define prevalence threshold as 10% of total samples ~ set of replicates
prevalenceThreshold = 0.10 * nsamples(s16sV3V5.1)
prevalenceThreshold
## [1] 4.8
# Execute prevalence filter, using `prune_taxa()` function
keepTaxa = rownames(prevelancedf1)[(prevelancedf1$Prevalence >= prevalenceThreshold)]
length(keepTaxa)
## [1] 932
s16sV3V5.2 = prune_taxa(keepTaxa, s16sV3V5.1)
s16sV3V5.2
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 932 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 932 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
Agglomerate taxa at the Genus level (combine all with the same name) keeping all taxa without genus level assignment
length(get_taxa_unique(s16sV3V5.2, taxonomic.rank = "Genus"))
## [1] 759
s16sV3V5.3 = tax_glom(s16sV3V5.2, "Genus", NArm = FALSE)
s16sV3V5.3
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 932 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 932 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
## out of curiosity how many "reads" does this leave us at???
sum(colSums(otu_table(s16sV3V5.3)))
## [1] 2682008
Now lets filter out samples (outliers and low performing samples)
Do some simple ordination looking for outlier samples, first we variance stabilize the data with a log transform, the perform PCoA using bray’s distances
logt = transform_sample_counts(s16sV3V5.3, function(x) log(1 + x) )
out.pcoa.logt <- ordinate(logt, method = "MDS", distance = "bray")
evals <- out.pcoa.logt$values$Eigenvalues
plot_ordination(logt, out.pcoa.logt, type = "samples",
color = "Treatment", shape = "Timepoint") + labs(col = "Treatment") +
coord_fixed(sqrt(evals[2] / evals[1]))
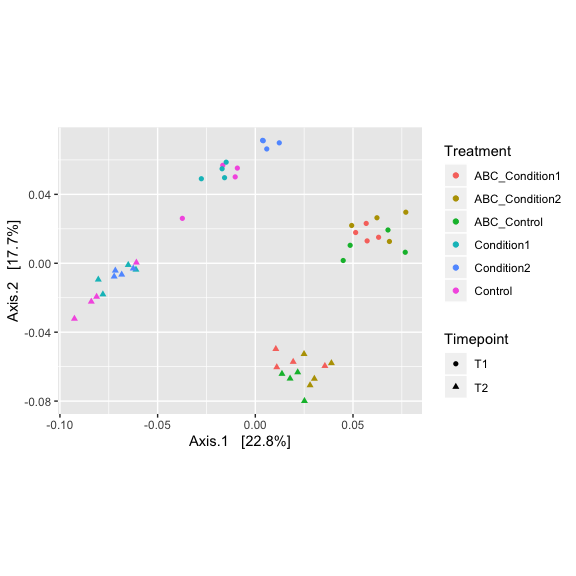
You could also use the MDS method of ordination here, edit the code to do so. Can also edit the distance method used to jaccard, jsd, euclidean. Play with changing those parameters
#Can view the distance method options with
?distanceMethodList
# can veiw the oridinate methods with
?ordinate
Show taxa proportions per sample (quickplot)
grid.arrange(nrow = 3,
qplot(as(otu_table(logt),"matrix")[, "sample1"], geom = "histogram", bins=30) +
xlab("Relative abundance"),
qplot(as(otu_table(logt),"matrix")[, "sample34"], geom = "histogram", bins=30) +
xlab("Relative abundance"),
qplot(as(otu_table(logt),"matrix")[, "sample44"], geom = "histogram", bins=30) +
xlab("Relative abundance")
)
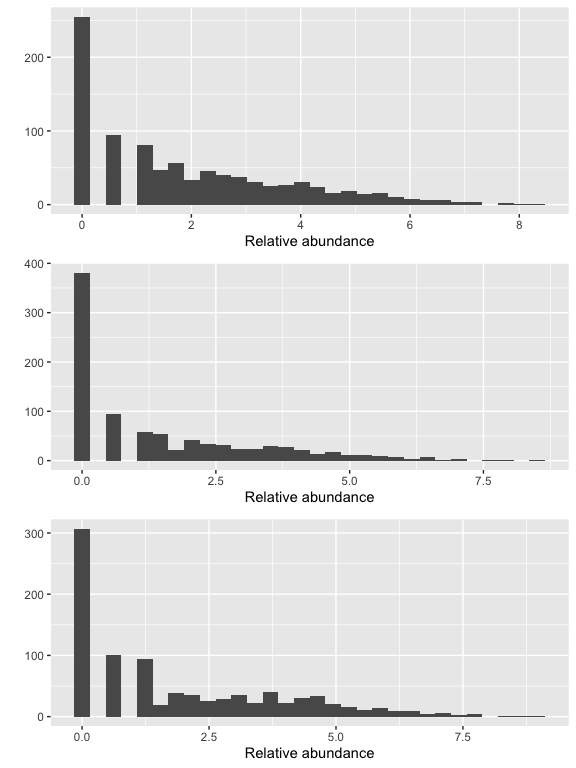
# if you needed to remove candidate outliers, can use the below to remove sample Slashpile18
#s16sV3V5.pruned <- prune_samples(sample_names(s16sV3V5.3) != c("sample1","sample2"), s16sV3V5.3)
Look for low perfroming samples
qplot(colSums(otu_table(s16sV3V5.3)),bins=30) + xlab("Logged counts-per-sample")
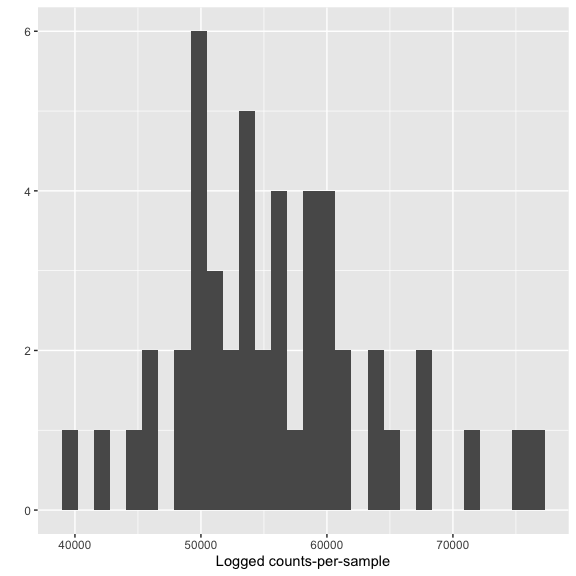
s16sV3V5.4 <- prune_samples(sample_sums(s16sV3V5.3)>=10000, s16sV3V5.3)
s16sV3V5.4
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 932 taxa and 48 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 4 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 932 taxa by 6 taxonomic ranks ]
Investigate transformations. We transform microbiome count data to account for differences in library size, variance, scale, etc.
- RLE - is the scaling factor method proposed by Anders and Huber (2010). We call it “relative log expression”, as median library is calculated from the geometric mean of all columns and the median ratio of each sample to the median library is taken as the scale factor.
## for Firmictures
plot_abundance = function(physeq, meta, title = "",
Facet = "Order", Color = "Order"){
# Arbitrary subset, based on Phylum, for plotting
p1f = subset_taxa(physeq, Phylum %in% c("p__Firmicutes"))
mphyseq = psmelt(p1f)
mphyseq <- subset(mphyseq, Abundance > 0)
ggplot(data = mphyseq, mapping = aes_string(x = meta,y = "Abundance",
color = Color, fill = Color)) +
geom_violin(fill = NA) +
geom_point(size = 1, alpha = 0.3,
position = position_jitter(width = 0.3)) +
facet_wrap(facets = Facet) + scale_y_log10()+
theme(legend.position="none")
}
# transform counts into "relative abundances"
s16sV3V5.4ra = transform_sample_counts(s16sV3V5.4, function(x){x / sum(x)})
# transform counts into "hellinger standardized counts"
s16sV3V5.4hell <- s16sV3V5.4
otu_table(s16sV3V5.4hell) <- otu_table(decostand(otu_table(s16sV3V5.4hell), method = "hellinger"), taxa_are_rows=TRUE)
# RLE counts
s16sV3V5.4RLE <- s16sV3V5.4
RLE_normalization <- function(phyloseq){
prior.count = 1
count_scale = median(sample_sums(phyloseq))
m = as(otu_table(phyloseq), "matrix")
d = DGEList(counts=m, remove.zeros = FALSE)
z = calcNormFactors(d, method="RLE")
y <- as.matrix(z)
lib.size <- z$samples$lib.size * z$samples$norm.factors
## rescale to median sample count
out <- round(count_scale * sweep(y,MARGIN=2, STATS=lib.size,FUN = "/"))
dimnames(out) <- dimnames(y)
out
}
otu_table(s16sV3V5.4RLE) <- otu_table(RLE_normalization(s16sV3V5.4), taxa_are_rows=TRUE)
s16sV3V5.4logRLE = transform_sample_counts(s16sV3V5.4RLE, function(x){ log2(x +1)})
plotOriginal = plot_abundance(s16sV3V5.4, "Treatment", title="original")
plotRelative = plot_abundance(s16sV3V5.4ra, "Treatment", title="relative")
plotHellinger = plot_abundance(s16sV3V5.4hell, "Treatment", title="Hellinger")
plotLogRLE = plot_abundance(s16sV3V5.4logRLE, "Treatment", title="Log")
# Combine each plot into one graphic.
grid.arrange(nrow = 4, plotOriginal, plotRelative, plotHellinger, plotLogRLE)
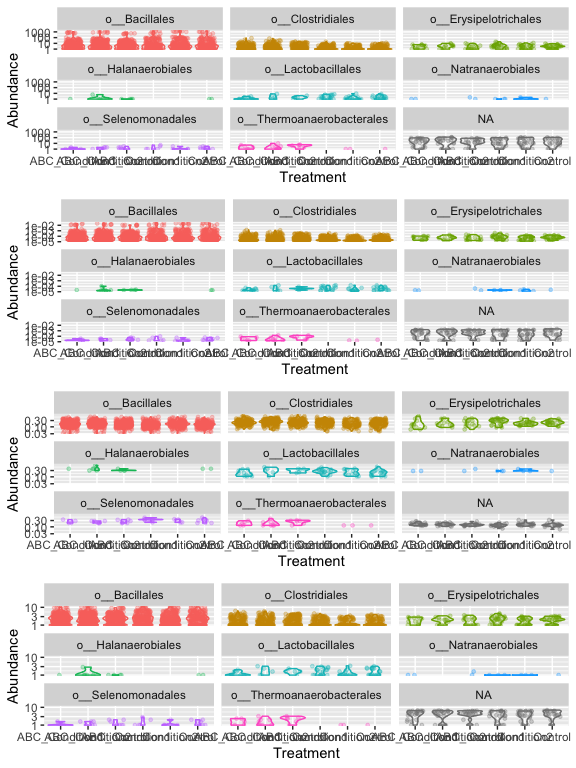
[Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics] (https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-017-0237-y)
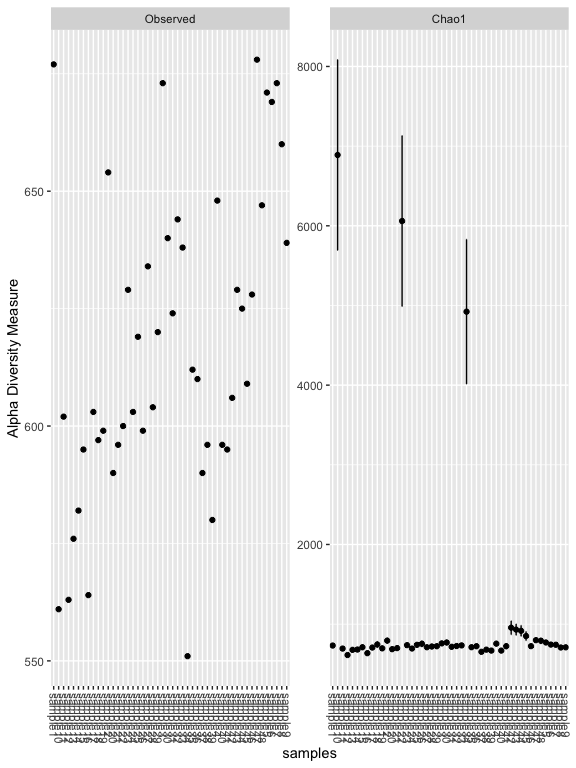
plot_richness(s16sV3V5.4RLE, measures=c("Observed","Chao1"))
## Warning: Removed 48 rows containing missing values (geom_errorbar).
plot_richness(s16sV3V5.4RLE, x = "Treatment", color="Timepoint", measures=c("Chao1", "Shannon"))
## Warning: Removed 48 rows containing missing values (geom_errorbar).

# Other Richness measures, "Observed", "Chao1", "ACE", "Shannon", "Simpson", "InvSimpson", "Fisher" try some of these others.
er <- estimate_richness(s16sV3V5.4RLE, measures=c("Chao1", "Shannon"))
res.aov <- aov(er$Shannon ~ Treatment + Timepoint, data = as(sample_data(s16sV3V5.4RLE),"data.frame"))
# Summary of the analysis
summary(res.aov)
## Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
## Treatment 5 0.1092 0.02185 8.072 2.26e-05 ***
## Timepoint 1 0.2078 0.20776 76.761 6.13e-11 ***
## Residuals 41 0.1110 0.00271
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Graphical Summaries
# Subset dataset by phylum
s16sV3V5.4RLE_acidob = subset_taxa(s16sV3V5.4RLE, Phylum=="p__Acidobacteria")
title = "plot_bar; Acidobacteria-only"
plot_bar(s16sV3V5.4RLE_acidob, "Treatment", "Abundance", "Family", title=title)
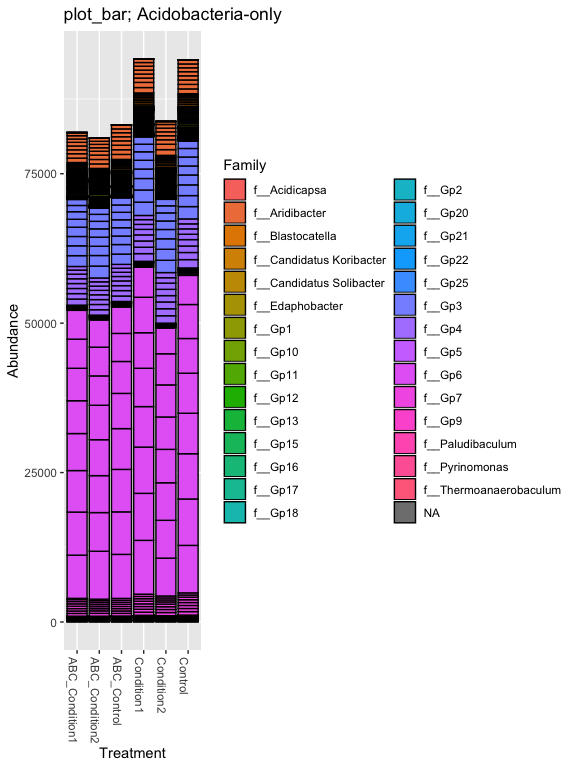
prop = transform_sample_counts(s16sV3V5.4, function(x) x / sum(x) )
keepTaxa <- ((apply(otu_table(prop) >= 0.005,1,sum,na.rm=TRUE) > 2) | (apply(otu_table(prop) >= 0.05, 1, sum,na.rm=TRUE) > 0))
table(keepTaxa)
## keepTaxa
## FALSE TRUE
## 872 60
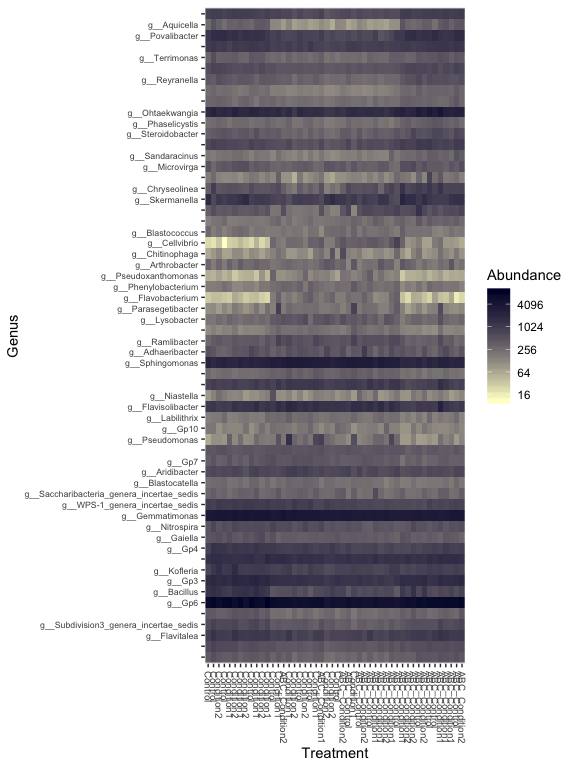
s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim <- prune_taxa(keepTaxa,s16sV3V5.4RLE)
plot_heatmap(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, "PCoA", distance="bray", sample.label="Treatment", taxa.label="Genus", low="#FFFFCC", high="#000033", na.value="white")
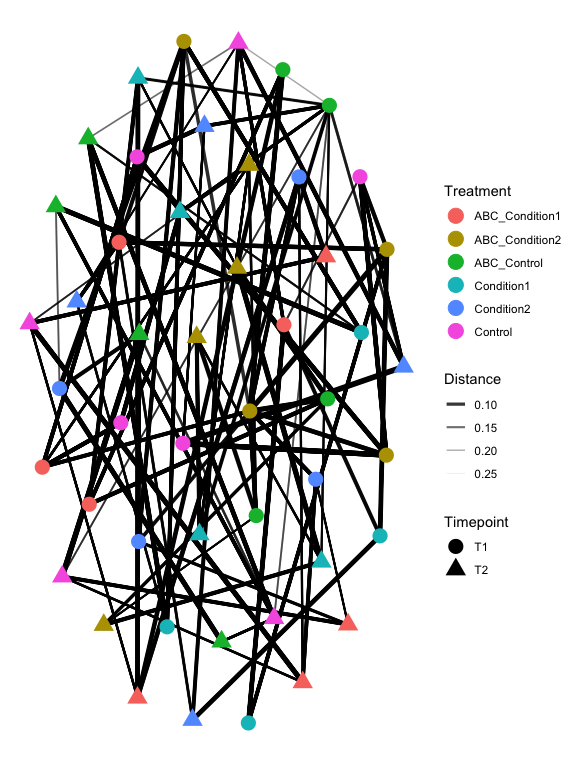
plot_net(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, maxdist=0.4, color="Treatment", shape="Timepoint")
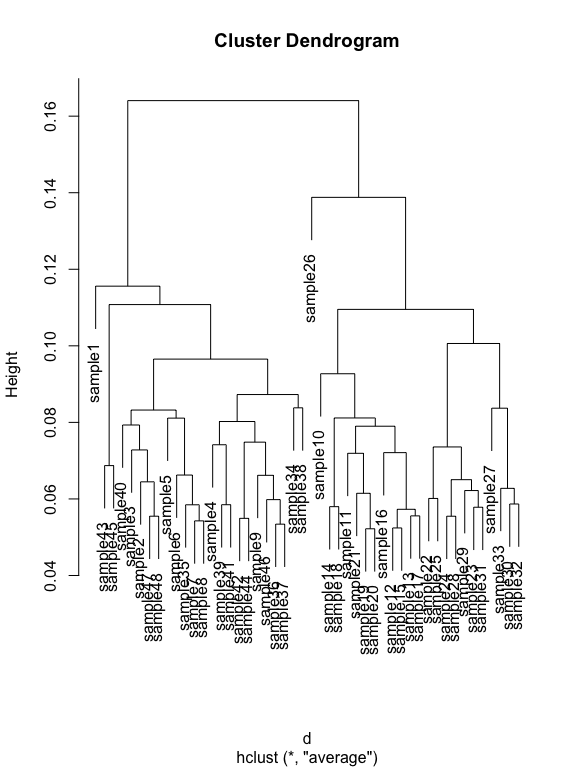
hell.tip.labels <- as(get_variable(s16sV3V5.4RLE, "Treatment"), "character")
# This is the actual hierarchical clustering call, specifying average-linkage clustering
d <- distance(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, method="bray", type="samples")
RLE.hclust <- hclust(d, method="average")
plot(RLE.hclust)
#Lets write out a plot
pdf("My_dendro.pdf", width=7, height=7, pointsize=8)
plot(RLE.hclust)
dev.off()
## quartz_off_screen
## 2
png("My_dendro.png", width = 7, height = 7, res=300, units = "in")
plot(RLE.hclust)
dev.off()
## quartz_off_screen
## 2
Ordination
v4.RLE.ord <- ordinate(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, "NMDS", "bray")
## Square root transformation
## Wisconsin double standardization
## Run 0 stress 0.09763903
## Run 1 stress 0.09764394
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.0007765653 max resid 0.003487272
## ... Similar to previous best
## Run 2 stress 0.09756916
## ... New best solution
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.006211429 max resid 0.03783506
## Run 3 stress 0.1183573
## Run 4 stress 0.09763896
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.006244267 max resid 0.03801658
## Run 5 stress 0.09764042
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.006300215 max resid 0.03833707
## Run 6 stress 0.1183573
## Run 7 stress 0.09764753
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.006422066 max resid 0.03872499
## Run 8 stress 0.116453
## Run 9 stress 0.09756901
## ... New best solution
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.0004025685 max resid 0.001596649
## ... Similar to previous best
## Run 10 stress 0.116453
## Run 11 stress 0.09756958
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.0001505171 max resid 0.0007177248
## ... Similar to previous best
## Run 12 stress 0.114047
## Run 13 stress 0.1183522
## Run 14 stress 0.1286158
## Run 15 stress 0.118443
## Run 16 stress 0.1183573
## Run 17 stress 0.1184438
## Run 18 stress 0.09789638
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.008618325 max resid 0.04188829
## Run 19 stress 0.09756889
## ... New best solution
## ... Procrustes: rmse 0.0003496162 max resid 0.001412773
## ... Similar to previous best
## Run 20 stress 0.1183573
## *** Solution reached
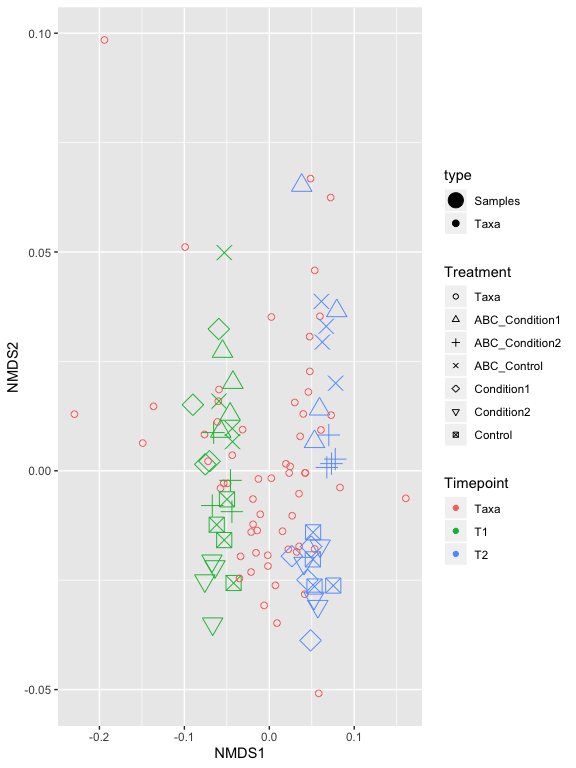
p1 = plot_ordination(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, v4.RLE.ord, type="taxa", color="Phylum", title="taxa")
print(p1)
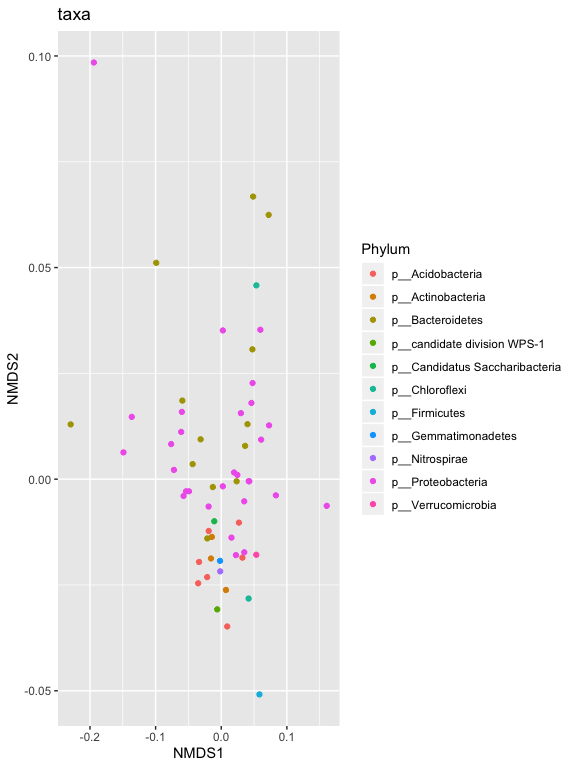
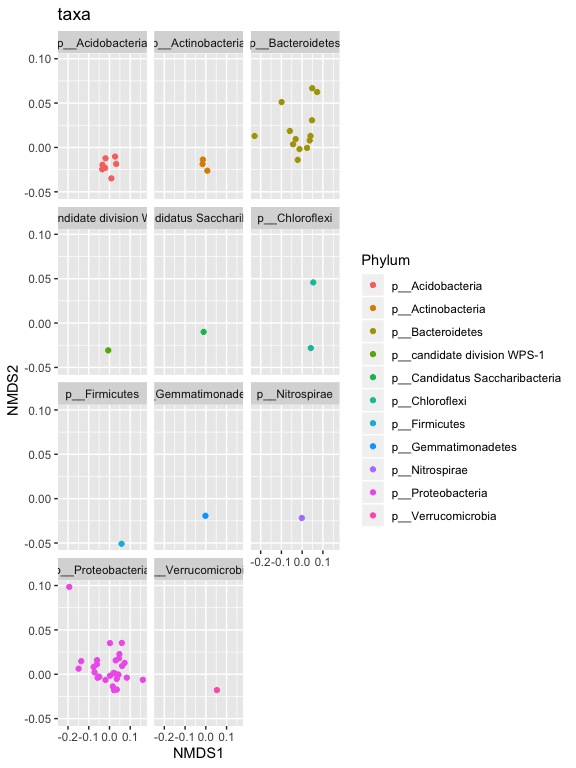
p1 + facet_wrap(~Phylum, 5)
p2 = plot_ordination(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, v4.RLE.ord, type="samples", color="Timepoint", shape="Treatment")
p2
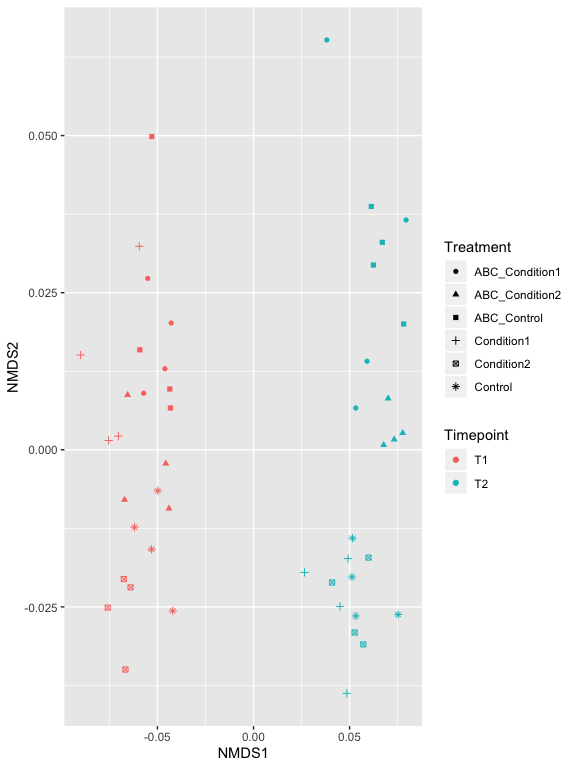
p2 + geom_polygon(aes(fill=Treatment)) + geom_point(size=5) + ggtitle("samples")
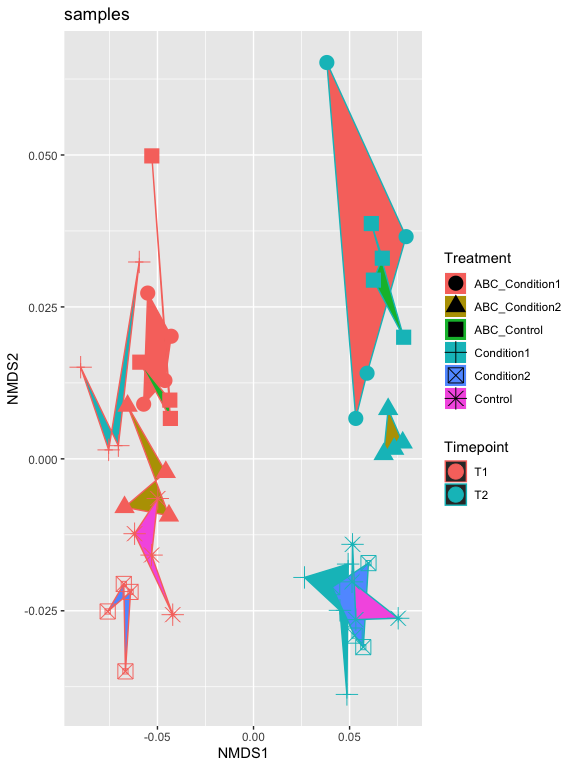
p2
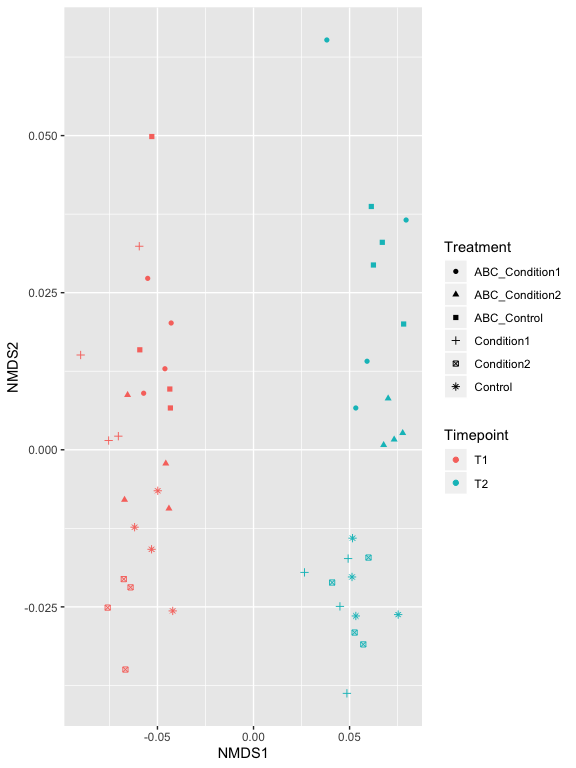
p2 = plot_ordination(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim, v4.RLE.ord, type="biplot", color="Timepoint", shape="Treatment") +
scale_shape_manual(values=1:7)
p2
write.table(otu_table(s16sV3V5.4RLE_trim), file = "RLE_stand_results_otu.txt",sep="\t")
Now try doing oridination with other transformations, such as relative abundance, log. Also looks and see if you can find any trends in the variable Dist_from_edge.
Differential Abundances
For differential abundances we use RNAseq pipeline EdgeR and limma voom.
m = as(otu_table(s16sV3V5.4), "matrix")
# Define gene annotations (`genes`) as tax_table
taxonomy = tax_table(s16sV3V5.4, errorIfNULL=FALSE)
if( !is.null(taxonomy) ){
taxonomy = data.frame(as(taxonomy, "matrix"))
}
# Now turn into a DGEList
d = DGEList(counts=m, genes=taxonomy, remove.zeros = TRUE)
## reapply filter
prop = transform_sample_counts(s16sV3V5.4, function(x) x / sum(x) )
keepTaxa <- ((apply(otu_table(prop) >= 0.005,1,sum,na.rm=TRUE) > 2) | (apply(otu_table(prop) >= 0.05, 1, sum,na.rm=TRUE) > 0))
table(keepTaxa)
## keepTaxa
## FALSE TRUE
## 872 60
d <- d[keepTaxa,]
# Calculate the normalization factors
z = calcNormFactors(d, method="RLE")
# Check for division by zero inside `calcNormFactors`
if( !all(is.finite(z$samples$norm.factors)) ){
stop("Something wrong with edgeR::calcNormFactors on this data,
non-finite $norm.factors, consider changing `method` argument")
}
plotMDS(z, col = as.numeric(factor(sample_data(s16sV3V5.4)$Treatment)), labels = sample_names(s16sV3V5.4), cex=0.5)
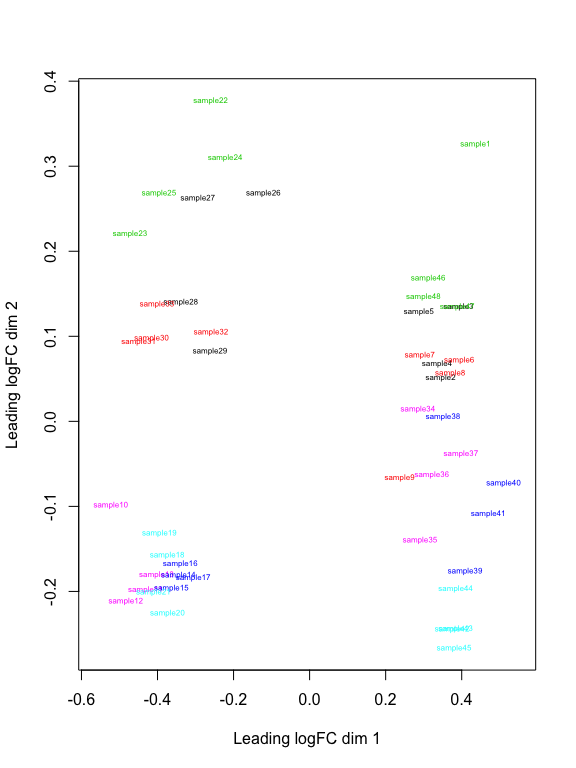
# Creat a model based on Treatment and depth
mm <- model.matrix( ~ Treatment + Timepoint, data=data.frame(as(sample_data(s16sV3V5.4),"matrix"))) # specify model with no intercept for easier contrasts
mm
## (Intercept) TreatmentABC_Condition2 TreatmentABC_Control
## sample1 1 0 1
## sample10 1 0 0
## sample11 1 0 0
## sample12 1 0 0
## sample13 1 0 0
## sample14 1 0 0
## sample15 1 0 0
## sample16 1 0 0
## sample17 1 0 0
## sample18 1 0 0
## sample19 1 0 0
## sample2 1 0 0
## sample20 1 0 0
## sample21 1 0 0
## sample22 1 0 1
## sample23 1 0 1
## sample24 1 0 1
## sample25 1 0 1
## sample26 1 0 0
## sample27 1 0 0
## sample28 1 0 0
## sample29 1 0 0
## sample3 1 0 0
## sample30 1 1 0
## sample31 1 1 0
## sample32 1 1 0
## sample33 1 1 0
## sample34 1 0 0
## sample35 1 0 0
## sample36 1 0 0
## sample37 1 0 0
## sample38 1 0 0
## sample39 1 0 0
## sample4 1 0 0
## sample40 1 0 0
## sample41 1 0 0
## sample42 1 0 0
## sample43 1 0 0
## sample44 1 0 0
## sample45 1 0 0
## sample46 1 0 1
## sample47 1 0 1
## sample48 1 0 1
## sample5 1 0 0
## sample6 1 1 0
## sample7 1 1 0
## sample8 1 1 0
## sample9 1 1 0
## TreatmentCondition1 TreatmentCondition2 TreatmentControl
## sample1 0 0 0
## sample10 0 0 1
## sample11 0 0 1
## sample12 0 0 1
## sample13 0 0 1
## sample14 1 0 0
## sample15 1 0 0
## sample16 1 0 0
## sample17 1 0 0
## sample18 0 1 0
## sample19 0 1 0
## sample2 0 0 0
## sample20 0 1 0
## sample21 0 1 0
## sample22 0 0 0
## sample23 0 0 0
## sample24 0 0 0
## sample25 0 0 0
## sample26 0 0 0
## sample27 0 0 0
## sample28 0 0 0
## sample29 0 0 0
## sample3 0 0 0
## sample30 0 0 0
## sample31 0 0 0
## sample32 0 0 0
## sample33 0 0 0
## sample34 0 0 1
## sample35 0 0 1
## sample36 0 0 1
## sample37 0 0 1
## sample38 1 0 0
## sample39 1 0 0
## sample4 0 0 0
## sample40 1 0 0
## sample41 1 0 0
## sample42 0 1 0
## sample43 0 1 0
## sample44 0 1 0
## sample45 0 1 0
## sample46 0 0 0
## sample47 0 0 0
## sample48 0 0 0
## sample5 0 0 0
## sample6 0 0 0
## sample7 0 0 0
## sample8 0 0 0
## sample9 0 0 0
## TimepointT2
## sample1 0
## sample10 1
## sample11 1
## sample12 1
## sample13 1
## sample14 1
## sample15 1
## sample16 1
## sample17 1
## sample18 1
## sample19 1
## sample2 0
## sample20 1
## sample21 1
## sample22 1
## sample23 1
## sample24 1
## sample25 1
## sample26 1
## sample27 1
## sample28 1
## sample29 1
## sample3 0
## sample30 1
## sample31 1
## sample32 1
## sample33 1
## sample34 0
## sample35 0
## sample36 0
## sample37 0
## sample38 0
## sample39 0
## sample4 0
## sample40 0
## sample41 0
## sample42 0
## sample43 0
## sample44 0
## sample45 0
## sample46 0
## sample47 0
## sample48 0
## sample5 0
## sample6 0
## sample7 0
## sample8 0
## sample9 0
## attr(,"assign")
## [1] 0 1 1 1 1 1 2
## attr(,"contrasts")
## attr(,"contrasts")$Treatment
## [1] "contr.treatment"
##
## attr(,"contrasts")$Timepoint
## [1] "contr.treatment"
y <- voom(d, mm, plot = T)
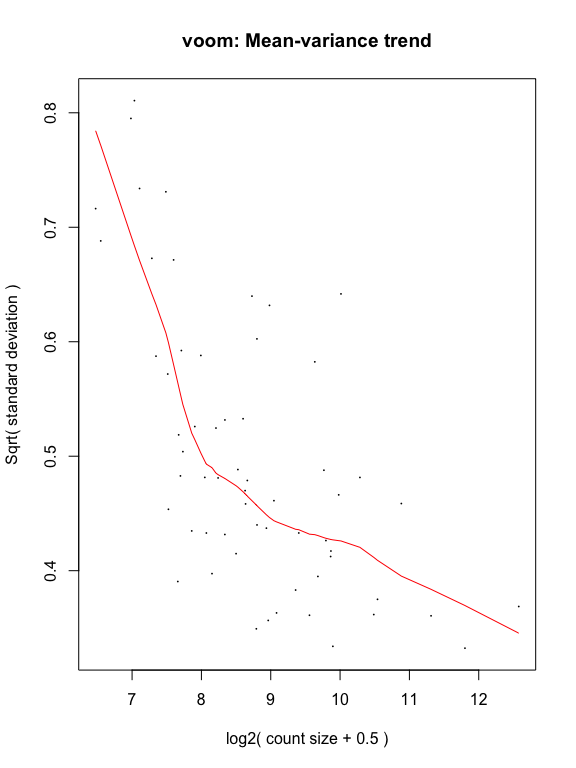
fit <- lmFit(y, mm)
head(coef(fit))
## (Intercept) TreatmentABC_Condition2 TreatmentABC_Control
## Taxa_00004 11.42021 0.56154953 0.247251333
## Taxa_00028 14.43708 0.09255719 0.004571592
## Taxa_00031 13.57321 0.04341135 0.200015067
## Taxa_00032 11.90593 0.06808778 0.201142692
## Taxa_00033 13.78071 -0.01281357 -0.053679539
## Taxa_00036 16.58393 -0.01195907 0.010459057
## TreatmentCondition1 TreatmentCondition2 TreatmentControl
## Taxa_00004 0.2225633 0.33218576 0.6937022
## Taxa_00028 0.2066517 0.18367808 0.2417164
## Taxa_00031 0.1464268 0.22360593 0.1845047
## Taxa_00032 0.4280512 0.42465403 0.4160526
## Taxa_00033 0.2197528 0.45398019 0.3521470
## Taxa_00036 0.1600282 -0.03887503 0.1554179
## TimepointT2
## Taxa_00004 -0.47590364
## Taxa_00028 0.31347126
## Taxa_00031 -0.25043174
## Taxa_00032 -0.23676668
## Taxa_00033 0.06211118
## Taxa_00036 0.24498846
# single contrast comparing Timepoint 5 - 20
contr <- makeContrasts(TimpointT2vT1 = "TimepointT2",
levels = colnames(coef(fit)))
## Warning in makeContrasts(TimpointT2vT1 = "TimepointT2", levels =
## colnames(coef(fit))): Renaming (Intercept) to Intercept
tmp <- contrasts.fit(fit, contr)
## Warning in contrasts.fit(fit, contr): row names of contrasts don't match
## col names of coefficients
tmp <- eBayes(tmp)
tmp2 <- topTable(tmp, coef=1, sort.by = "P", n = Inf)
tmp2$Taxa <- rownames(tmp2)
tmp2 <- tmp2[,c("Taxa","logFC","AveExpr","P.Value","adj.P.Val")]
length(which(tmp2$adj.P.Val < 0.05)) # number of Differentially abundant taxa
## [1] 48
# 48
sigtab = cbind(as(tmp2, "data.frame"), as(tax_table(s16sV3V5.4)[rownames(tmp2), ], "matrix"))
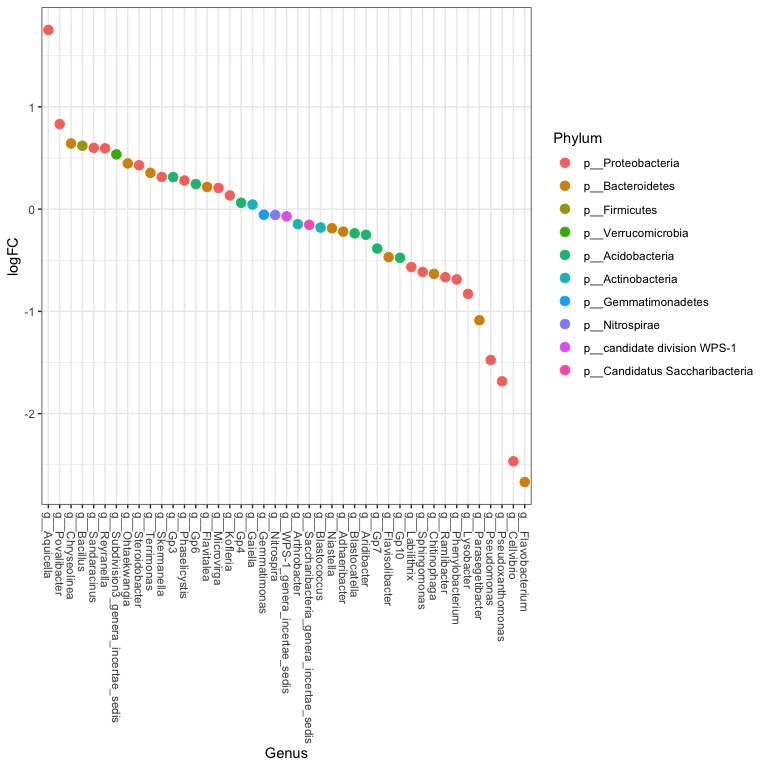
One last plot
theme_set(theme_bw())
scale_fill_discrete <- function(palname = "Set1", ...) {
scale_fill_brewer(palette = palname, ...)
}
sigtabgen = subset(sigtab, !is.na(Genus))
# Phylum order
x = tapply(sigtabgen$logFC, sigtabgen$Phylum, function(x) max(x))
x = sort(x, TRUE)
sigtabgen$Phylum = factor(as.character(sigtabgen$Phylum), levels = names(x))
# Genus order
x = tapply(sigtabgen$logFC, sigtabgen$Genus, function(x) max(x))
x = sort(x, TRUE)
sigtabgen$Genus = factor(as.character(sigtabgen$Genus), levels = names(x))
ggplot(sigtabgen, aes(x = Genus, y = logFC, color = Phylum)) + geom_point(size=3) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = -90, hjust = 0, vjust = 0.5))