Running the dbcAmplicons pipeline
This document assumes Dataset and Metadata has been completed.
Lets login and request an interactive session on the clusters
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
srun -t 08:00:00 -c 4 -n 1 --mem 8000 --partition production --account workshop --reservation workshop --pty /bin/bash
After getting onto a cluster node, source our dbcAmplicons environment
source /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example/src/dbcA_profile
The goal is to process raw Illumina sequence reads to abundance tables for the 16sV3-V5 amplicon set. To do so we first need to
- Have all the software installed and working, and
- Have the Illumina sequence data within our project folder (mca_example).
- Have the input metadata files: barcodes, primers, and samples.
- Perform amplicon processing with dbcAmplicons includes the following steps: 1. preprocessing 2. join 3. classify 4. abundances.
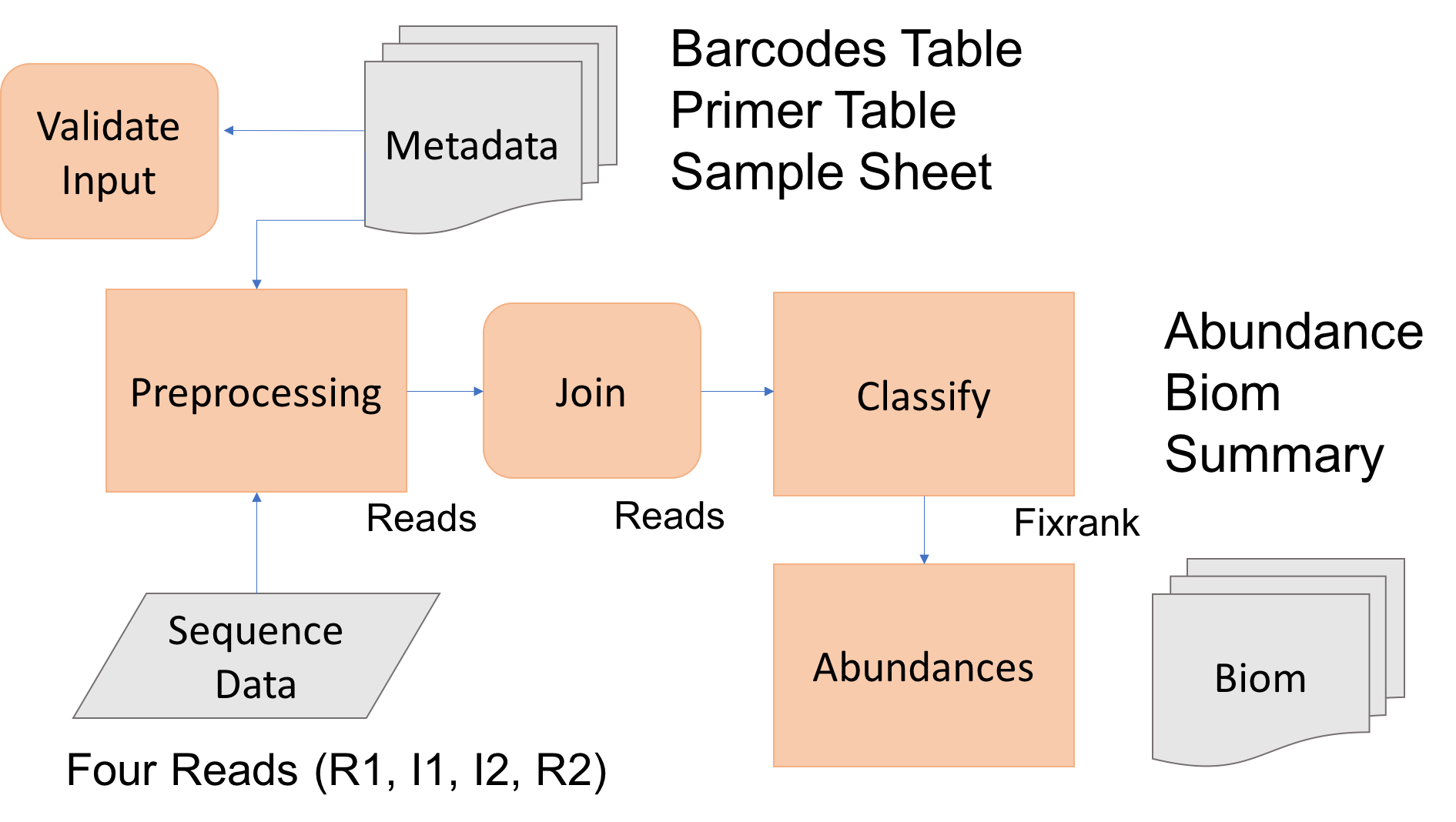
Today we’ll process at least one amplicon set to completion.
Change directory into the workshops space
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
ls
you should see 4 directories: bin, Illumina_Reads, metadata and src
Lets verify the software is accessible
dbcVersionReport.sh
you should see the version info for dbcAmplicons, flash2 and RDP.
1. Lets validate our input files using dbcAmplicons Validate:
Look at the help documentation first
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcAmplicons validate -h
dbcAmplicons validate -B metadata/BarcodeTable.txt -P metadata/PrimerTable.txt -S metadata/workshopSamplesheet.txt
If there are any errors, fix them (can do so in nano) and validate again.
Once we are sure our input files are ok, pass validation
2. Lets Preprocess the data, should talk less than 1 hour. We will be putting all intermediate output to a folder Workshop.intermediate
Look at the help documentation first
dbcAmplicons preprocess -h
First lets ‘test’ preprocessing, by only running the first ‘batch’ of reads
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcAmplicons preprocess -B metadata/BarcodeTable.txt -P metadata/PrimerTable.txt -S metadata/workshopSamplesheet.txt -O Workshop.intermediate -1 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_I1_001.fastq.gz -3 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_I2_001.fastq.gz -4 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz --test > preprocess.log
View preprocess.log and the file Identified_barcodes.txt, make sure the results make sense.
cat preprocess.log
cat Workshop.intermediate/Identified_Barcodes.txt
Lets see what it looks like when you get the primer orientation incorrect. Try running the above but add the parameter, –I1 asis. Then look at the output again.
Now run all reads, should take less than 1 hour (~30 minutes).
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcAmplicons preprocess -B metadata/BarcodeTable.txt -P metadata/PrimerTable.txt -S metadata/workshopSamplesheet.txt -O Workshop.intermediate -1 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_I1_001.fastq.gz -3 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_I2_001.fastq.gz -4 Illumina_Reads/MCAWorkshopDataset_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz > preprocess.log
Again view the output to make sure it makes sense
cat preprocess.log
cat Workshop.intermediate/Identified_Barcodes.txt
Finally, look at the output in the Workshop.intermediate folder, how many subfolders are there? What do these correspond to? What is inside each folder? View a few reads in one of the files.
3. Next, lets merge/join the read pairs, should take less than 10 minutes
View the help documentation and run join
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcAmplicons join -h
dbcAmplicons join -t 4 -O Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5 -1 Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5_R1.fastq.gz > join-16sV3V5.log
view the log
cat join-16sV3V5.log
Try changing the parameter –max-mismatch-density, first to 0.1, then to 0.5, how do they differ.
If you prefer the default, run join again with defaults. dbcAmplicons join also produces two histogram files (.hist and .histogram) in the output folder. View these files (can use cat, less, more, etc.). What do you see?
4. Classify the merged reads using RDP, should take less than 3 hours.
View the help documentation and run classify
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcAmplicons classify -h
dbcAmplicons classify -p 4 --gene 16srrna -U Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5.extendedFrags.fastq.gz -O Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5
classify produces a fixrank file, view the first 6 lines of the output file
head Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5.fixrank
For the other amplicons what parameters in classify would need to be changed?
During the next week try running classify on the original preprocessed reads, skipping join, how do the results compare to the overlapped set?
5. Finally produce Abundance tables, should take less than 20 minutes
Lets make a new folder for the final output results.
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
mkdir Workshop.results
View the help documentation and generate the results. When you provide dbcAmplicons abundance with a sample sheet it will include any additional metadata (extra columns added to the sample sheet) into the biom file for downstream processing.
dbcAmplicons abundance -h
dbcAmplicons abundance -S metadata/workshopSamplesheet.txt -O Workshop.results/16sV3V5 -F Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5.fixrank --biom > abundance.16sV3V5.log
cat abundance.16sV3V5.log
Try changing the -r parameter see what changes? what about the -t parameter? How about -m and -M? Look at the histogram generated in join, what min/max would you choose, how does it affect results? Once done playing rerun the above to get the final biom file for the next phase of analysis.
dbcAmplicons abundance command above (with –biom) produces four files: abundance, proportions, tax_info and biom files. Using cat, less, or more view these files. What do you see?
6. Split Reads by samples
For downstream processing in another application (post preprocessing/merging), or for submission to the SRA. splitReadsBySample produces SRA compatible output (read names) for each samples. Splits the reads by sample.
view the help documentation then run, placing output into the folder SplitBySample/16sV3V5
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
splitReadsBySample.py -h
splitReadsBySample.py -O SplitBySample/16sV3V5 -1 Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5_R1.fastq.gz -2 Workshop.intermediate/MCA_Workshop/workshop-16SV3V5_R2.fastq.gz
View the output folder, what do you see?
7. Write out the software versions to a file in the folder for records keeping.
cd /share/workshop/$USER/mca_example
dbcVersionReport.sh &> VersionInfo.txt
FYI
dbcAmplicons screen can be used when you want to remove read contaminants. Can be ran either before or after dbcAmplicons join. You provide a reference fasta file to screen and it will remove any reads that map to any sequence in that file.
dbcAmplicons screen -h
dbcAmplicons extract can be used when you want to isolate sequencing reads from a specific taxonomic group for additional processing.
dbcAmplicons extract -h
